Mending a Broken Heart: Treatment of Stress-Induced Heart Failure after Solid Organ Transplantation
- PMID: 29670765
- PMCID: PMC5835255
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9739236
Mending a Broken Heart: Treatment of Stress-Induced Heart Failure after Solid Organ Transplantation
Abstract
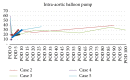
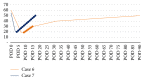
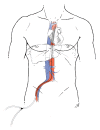
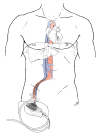
Stress-induced heart failure, also known as Broken Heart Syndrome or Takotsubo Syndrome, is a phenomenon characterized as rare but well described in the literature, with increasing incidence. While more commonly associated with postmenopausal women with psychiatric disorders, this entity is found in the postoperative patient. The nonischemic cardiogenic shock manifests as biventricular failure with significant decreases in ejection fraction and cardiac function. In a review of over 3000 kidney and liver transplantations over the course of 17 years within two transplant centers, we describe a series of 7 patients with Takotsubo Syndrome after solid organ transplantation. Furthermore, we describe a novel approach of successfully treating the transient, though potentially fatal, cardiogenic shock with a percutaneous ventricular assistance device in two liver transplant patients, while treating one kidney transplant patient medically and the remaining four liver transplant patients with an intra-aortic balloon pump. We describe our experience with Takotsubo's Syndrome and compare the three modalities of treatment and cardiac augmentation. Our series is novel in introducing the percutaneous ventricular assist device as a more minimally invasive intervention in treating nonischemic heart failure in the solid organ transplant patient, while serving as a comprehensive overview of treatment modalities for stress-induced heart failure.
Figures

References
-
- Lyon A. R., Bossone E., Schneider B., et al. Current state of knowledge on takotsubo syndrome: a position statement from the taskforce on takotsubo syndrome of the heart failure association of the european society of cardiology. European Journal of Heart Failure. 2015;18(1):8–27. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.424. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

