Autism Spectrum Symptomatology in Children with Williams Syndrome Who Have Phrase Speech or Fluent Language
- PMID: 29671106
- PMCID: PMC6082683
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-018-3555-4
Autism Spectrum Symptomatology in Children with Williams Syndrome Who Have Phrase Speech or Fluent Language
Abstract
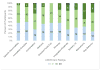
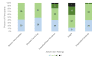
To characterize autism spectrum-related symptomatology in children with Williams syndrome (WS) with phrase speech or fluent language, the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule Module 2 or 3 was administered. The cutoff for autism spectrum was met by 35% (14/40) who completed Module 2 and 30% (18/60) who completed Module 3. Similarities and differences in socio-communicative strengths and weaknesses as a function of language ability were identified. Symptom severity was negatively associated with IQ for participants with phrase speech but not for those with fluent language. The findings suggest an elevated risk of ASD for individuals with WS relative to the general population and contribute to a more nuanced sense of the socio-communicative functioning of children with WS.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders; Intellectual disability; Social communication; Williams syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Autism Spectrum Symptomatology Among Children with Duplication 7q11.23 Syndrome.J Autism Dev Disord. 2018 Jun;48(6):1982-1994. doi: 10.1007/s10803-017-3439-z. J Autism Dev Disord. 2018. PMID: 29307037 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Interactive Behaviours in Parenting Children with Williams Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Relations with Emotional/Behavioural Problems.J Autism Dev Disord. 2019 Jan;49(1):216-226. doi: 10.1007/s10803-018-3715-6. J Autism Dev Disord. 2019. PMID: 30143949
-
Violations of Personal Space in Young People with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Williams Syndrome: Insights from the Social Responsiveness Scale.J Autism Dev Disord. 2015 Dec;45(12):4101-8. doi: 10.1007/s10803-015-2536-0. J Autism Dev Disord. 2015. PMID: 26206231
-
Neurodevelopmental Disorders Affecting Sociability: Recent Research Advances and Future Directions in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Williams Syndrome.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2018 Oct 17;18(12):94. doi: 10.1007/s11910-018-0902-y. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30328520 Review.
-
Language and communicative development in Williams syndrome.Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2007;13(1):3-15. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20140. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 17326109 Review.
Cited by
-
Cooperative Parent-Mediated Therapy in Children with Fragile X Syndrome and Williams Beuren Syndrome: A Pilot RCT Study of a Transdiagnostic Intervention-Preliminary Data.Brain Sci. 2021 Dec 23;12(1):8. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12010008. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 35053752 Free PMC article.
-
Rhythm and timing as vulnerabilities in neurodevelopmental disorders.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021 Oct 11;376(1835):20200327. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0327. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34420385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Social feedback enhances learning in Williams syndrome.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 4;13(1):164. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26055-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36599864 Free PMC article.
-
No transfer of arousal from other's eyes in Williams syndrome.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 26;13(1):18397. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45521-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37884631 Free PMC article.
-
Williams Syndrome, Human Self-Domestication, and Language Evolution.Front Psychol. 2019 Mar 18;10:521. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00521. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30936846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becerra AM. Patterns of early lexical and gestural development in children with Williams syndrome. Doctoral dissertation. 2016 Retrieved from http://ir.library.louisville.edu/etd/2407/
-
- Bloom P. The boy who loved too much: A true story of pathological friendliness. New York: Simon & Schuster; 2017. Comment on back cover of J. Latson (2017)
-
- Capirci O, Iverson J, Pizzuto E, Volterra V. Gestures and words during the transition to two-word speech. Journal of Child Language. 1996;43:917–929. doi: 10.1017/S0305000900008989. - DOI
-
- Constantino JN, Gruber CP. Manual for Social Responsiveness Scale. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services; 2005.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

