Autism Spectrum Symptomatology in Children with Williams Syndrome Who Have Phrase Speech or Fluent Language
- PMID: 29671106
- PMCID: PMC6082683
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-018-3555-4
Autism Spectrum Symptomatology in Children with Williams Syndrome Who Have Phrase Speech or Fluent Language
Abstract
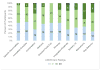
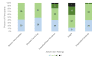
To characterize autism spectrum-related symptomatology in children with Williams syndrome (WS) with phrase speech or fluent language, the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule Module 2 or 3 was administered. The cutoff for autism spectrum was met by 35% (14/40) who completed Module 2 and 30% (18/60) who completed Module 3. Similarities and differences in socio-communicative strengths and weaknesses as a function of language ability were identified. Symptom severity was negatively associated with IQ for participants with phrase speech but not for those with fluent language. The findings suggest an elevated risk of ASD for individuals with WS relative to the general population and contribute to a more nuanced sense of the socio-communicative functioning of children with WS.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders; Intellectual disability; Social communication; Williams syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures



References
-
- Becerra AM. Patterns of early lexical and gestural development in children with Williams syndrome. Doctoral dissertation. 2016 Retrieved from http://ir.library.louisville.edu/etd/2407/
-
- Bloom P. The boy who loved too much: A true story of pathological friendliness. New York: Simon & Schuster; 2017. Comment on back cover of J. Latson (2017)
-
- Capirci O, Iverson J, Pizzuto E, Volterra V. Gestures and words during the transition to two-word speech. Journal of Child Language. 1996;43:917–929. doi: 10.1017/S0305000900008989. - DOI
-
- Constantino JN, Gruber CP. Manual for Social Responsiveness Scale. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services; 2005.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

