ncRNA-disease association prediction based on sequence information and tripartite network
- PMID: 29671405
- PMCID: PMC5907179
- DOI: 10.1186/s12918-018-0527-4
ncRNA-disease association prediction based on sequence information and tripartite network
Abstract
Background: Current technology has demonstrated that mutation and deregulation of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are associated with diverse human diseases and important biological processes. Therefore, developing a novel computational method for predicting potential ncRNA-disease associations could benefit pathologists in understanding the correlation between ncRNAs and disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. However, only a few studies have investigated these associations in pathogenesis.
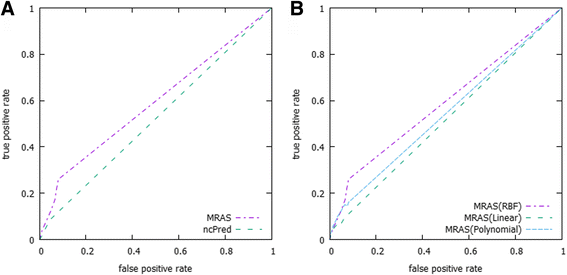
Results: This study utilizes a disease-target-ncRNA tripartite network, and computes prediction scores between each disease-ncRNA pair by integrating biological information derived from pairwise similarity based upon sequence expressions with weights obtained from a multi-layer resource allocation technique. Our proposed algorithm was evaluated based on a 5-fold-cross-validation with optimal kernel parameter tuning. In addition, we achieved an average AUC that varies from 0.75 without link cut to 0.57 with link cut methods, which outperforms a previous method using the same evaluation methodology. Furthermore, the algorithm predicted 23 ncRNA-disease associations supported by other independent biological experimental studies.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results demonstrate the capability and accuracy of predicting further biological significant associations between ncRNAs and diseases and highlight the importance of adding biological sequence information to enhance predictions.
Keywords: Resource allocation; Tripartite network; ncRNA-disease association predictions.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





Similar articles
-
ncPred: ncRNA-Disease Association Prediction through Tripartite Network-Based Inference.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014 Dec 12;2:71. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2014.00071. eCollection 2014. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25566534 Free PMC article.
-
Controllability Methods for Identifying Associations Between Critical Control ncRNAs and Human Diseases.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1912:289-300. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8982-9_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30635898 Review.
-
MNDR v2.0: an updated resource of ncRNA-disease associations in mammals.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D371-D374. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29106639 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring associations of non-coding RNAs in human diseases via three-matrix factorization with hypergraph-regular terms on center kernel alignment.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbaa409. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa409. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33443536
-
A Survey on Computational Methods for Investigation on ncRNA-Disease Association through the Mode of Action Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11498. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911498. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A lncRNA-disease association prediction tool development based on bridge heterogeneous information network via graph representation learning for family medicine and primary care.Front Genet. 2023 May 18;14:1084482. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1084482. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37274787 Free PMC article.
-
The computational approaches of lncRNA identification based on coding potential: Status quo and challenges.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Nov 19;18:3666-3677. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.030. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33304463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Methods and Applications for Identifying Disease-Associated lncRNAs as Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 4;21:156-171. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.05.018. Epub 2020 May 21. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32585624 Free PMC article.
-
Role of caprin-1 in carcinogenesis.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):15-21. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10295. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA in alcohol use disorder by affecting synaptic plasticity.Exp Brain Res. 2022 Feb;240(2):365-379. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06305-x. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Exp Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35028694 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

