Charting the unexplored extracellular matrix in cancer
- PMID: 29671911
- PMCID: PMC6031881
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12269
Charting the unexplored extracellular matrix in cancer
Abstract
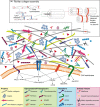
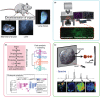
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is present in all solid tissues and considered a master regulator of cell behaviour and phenotype. The importance of maintaining the correct biochemical and biophysical properties of the ECM, and the subsequent regulation of cell and tissue homeostasis, is illustrated by the simple fact that the ECM is highly dysregulated in many different types of disease, especially cancer. The loss of tissue ECM homeostasis and integrity is seen as one of the hallmarks of cancer and typically defines transitional events in progression and metastasis. The vast majority of cancer studies place an emphasis on exploring the behaviour and intrinsic signalling pathways of tumour cells. Their goal was to identify ways to target intracellular pathways regulating cancer. Cancer progression and metastasis are powerfully influenced by the ECM and thus present a vast, unexplored repository of anticancer targets that we are only just beginning to tap into. Deconstructing the complexity of the tumour ECM landscape and identifying the interactions between the many cell types, soluble factors and extracellular-matrix proteins have proved challenging. Here, we discuss some of the emerging tools and platforms being used to catalogue and chart the ECM in cancer.
Keywords: cancer; extracellular matrix; imaging; metastasis; proteomics; remodelling.
© 2018 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2018 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The interplay between extracellular matrix remodelling and kinase signalling in cancer progression and metastasis.Cell Adh Migr. 2018;12(6):529-537. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2017.1405208. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29168660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matricellular proteins: priming the tumour microenvironment for cancer development and metastasis.Br J Cancer. 2013 Mar 5;108(4):755-61. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.592. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23322204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The matrix environmental and cell mechanical properties regulate cell migration and contribute to the invasive phenotype of cancer cells.Rep Prog Phys. 2019 Jun;82(6):064602. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ab1628. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Rep Prog Phys. 2019. PMID: 30947151 Review.
-
Dynamic matrisome: ECM remodeling factors licensing cancer progression and metastasis.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018 Dec;1870(2):207-228. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30316942 Review.
-
The Tumor Microenvironment: Focus on Extracellular Matrix.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1245:1-38. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-40146-7_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32266651 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of Key Genes and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Gastric Cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 22;2020:2862701. doi: 10.1155/2020/2862701. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32908877 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory role of metalloproteases in cancers: Current progress and future trends.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 16;13:1064033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1064033. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix Metalloproteases in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Key Drivers of Disease Progression?Biology (Basel). 2020 Apr 18;9(4):80. doi: 10.3390/biology9040080. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32325664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Extracellular Matrix: Its Composition, Function, Remodeling, and Role in Tumorigenesis.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Apr 5;8(2):146. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8020146. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37092398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of pancreatic extracellular matrix protein post-translational modifications via electrostatic repulsion-hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry.Mol Omics. 2021 Oct 11;17(5):652-664. doi: 10.1039/d1mo00104c. Mol Omics. 2021. PMID: 34318855 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

