P21-activated kinase 4 in pancreatic acinar cells is activated by numerous gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters and growth factors by novel signaling, and its activation stimulates secretory/growth cascades
- PMID: 29672153
- PMCID: PMC6139648
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00005.2018
P21-activated kinase 4 in pancreatic acinar cells is activated by numerous gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters and growth factors by novel signaling, and its activation stimulates secretory/growth cascades
Abstract
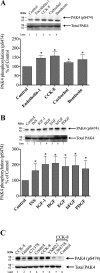
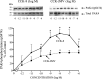
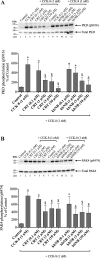
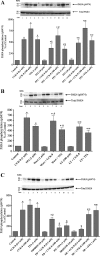
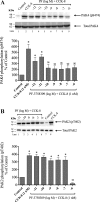
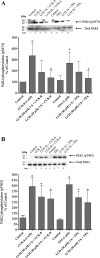
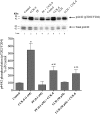
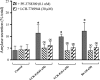
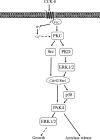
p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are highly conserved serine/threonine protein kinases, which are divided into two groups: group-I (PAKs1-3) and group-II (PAKs4-6). In various tissues, Group-II PAKs play important roles in cytoskeletal dynamics and cell growth as well as neoplastic development/progression. However, little is known about Group-II PAK's role in a number of physiological events, including their ability to be activated by gastrointestinal (GI) hormones/neurotransmitters/growth factors (GFs). We used rat pancreatic acini to explore the ability of GI hormones/neurotransmitters/GFs to activate Group-II-PAKs and the signaling cascades involved. Only PAK4 was detected in pancreatic acini. PAK4 was activated by endothelin, secretagogues-stimulating phospholipase C (bombesin, CCK-8, and carbachol), by pancreatic GFs (insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1, hepatocyte growth factor, epidermal growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and platelet-derived growth factor), and by postreceptor stimulants (12-O-tetradecanoylphobol-13-acetate and A23187 ). CCK-8 activation of PAK4 required both high- and low-affinity CCK1-receptor state activation. It was reduced by PKC-, Src-, p44/42-, or p38-inhibition but not with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-inhibitors and only minimally by thapsigargin. A protein kinase D (PKD)-inhibitor completely inhibited CCK-8-stimulated PKD-activation; however, stimulated PAK4 phosphorylation was only inhibited by 60%, demonstrating that it is both PKD-dependent and PKD-independent. PF-3758309 and LCH-7749944, inhibitors of PAK4, decreased CCK-8-stimulated PAK4 activation but not PAK2 activation. Each inhibited ERK1/2 activation and amylase release induced by CCK-8 or bombesin. These results show that PAK4 has an important role in modulating signal cascades activated by a number of GI hormones/neurotransmitters/GFs that have been shown to mediate both physiological/pathological responses in acinar cells. Therefore, in addition to the extensive studies on PAK4 in pancreatic cancer, PAK4 should also be considered an important signaling molecule for pancreatic acinar physiological responses and, in the future, should be investigated for a possible role in pancreatic acinar pathophysiological responses, such as in pancreatitis. NEW & NOTEWORTHY This study demonstrates that the only Group-II p21-activated kinase (PAK) in rat pancreatic acinar cells is PAK4, and thus differs from islets/pancreatic cancer. Both gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters stimulating PLC and pancreatic growth factors activate PAK4. With cholecystokinin (CCK), activation is PKC-dependent/-independent, requires both CCK1-R affinity states, Src, p42/44, and p38 activation. PAK4 activation is required for CCK-mediated p42/44 activation/amylase release. These results show PAK4 plays an important role in mediating CCK physiological signal cascades and suggest it may be a target in pancreatic acinar diseases besides cancer.
Keywords: CCK; bombesin; celluar calcium; pancreatic acini; protein kinase C; signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Important Role of p21-Activated Kinases in Pancreatic Exocrine Function.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jan 22;14(2):113. doi: 10.3390/biology14020113. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters and growth factors can activate P21 activated kinase 2 in pancreatic acinar cells by novel mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt A):2371-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.05.011. Epub 2015 May 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25979836 Free PMC article.
-
Group II p21-activated kinase, PAK4, is needed for activation of focal adhesion kinases, MAPK, GSK3, and β-catenin in rat pancreatic acinar cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):G490-G503. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00229.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31984786 Free PMC article.
-
The Src kinase Yes is activated in pancreatic acinar cells by gastrointestinal hormones/neurotransmitters, but not pancreatic growth factors, which stimulate its association with numerous other signaling molecules.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Aug;1823(8):1285-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.05.015. Epub 2012 May 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22617836 Free PMC article.
-
Cholecystokinin activates a variety of intracellular signal transduction mechanisms in rodent pancreatic acinar cells.Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002 Dec;91(6):297-303. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0773.2002.910606.x. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 12688372 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of p21-Activated Kinases in Cancer and Beyond: Where Are We Heading?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 16;9:641381. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.641381. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33796531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cofilin activation in pancreatic acinar cells plays a pivotal convergent role for mediating CCK-stimulated enzyme secretion and growth.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1147572. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1147572. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37138671 Free PMC article.
-
CCK Receptor Inhibition Reduces Pancreatic Tumor Fibrosis and Promotes Nanoparticle Delivery.Biomedicines. 2024 May 7;12(5):1024. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051024. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38790986 Free PMC article.
-
P-21 Activated Kinases in Liver Disorders.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 16;15(2):551. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020551. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Important Role of p21-Activated Kinases in Pancreatic Exocrine Function.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jan 22;14(2):113. doi: 10.3390/biology14020113. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001881 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

