miR-122 does not impact recognition of the HCV genome by innate sensors of RNA but rather protects the 5' end from the cellular pyrophosphatases, DOM3Z and DUSP11
- PMID: 29672716
- PMCID: PMC6007490
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky273
miR-122 does not impact recognition of the HCV genome by innate sensors of RNA but rather protects the 5' end from the cellular pyrophosphatases, DOM3Z and DUSP11
Abstract
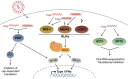
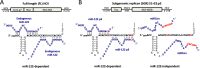
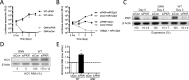
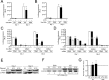
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) recruits two molecules of the liver-specific microRNA-122 (miR-122) to the 5' end of its genome. This interaction promotes viral RNA accumulation, but the precise mechanism(s) remain incompletely understood. Previous studies suggest that miR-122 is able to protect the HCV genome from 5' exonucleases (Xrn1/2), but this protection is not sufficient to account for the effect of miR-122 on HCV RNA accumulation. Thus, we investigated whether miR-122 was also able to protect the viral genome from innate sensors of RNA or cellular pyrophosphatases. We found that miR-122 does not play a protective role against recognition by PKR, RIG-I-like receptors, or IFITs 1 and 5. However, we found that knockdown of both the cellular pyrophosphatases, DOM3Z and DUSP11, was able to rescue viral RNA accumulation of subgenomic replicons in the absence of miR-122. Nevertheless, pyrophosphatase knockdown increased but did not restore viral RNA accumulation of full-length HCV RNA in miR-122 knockout cells, suggesting that miR-122 likely plays an additional role(s) in the HCV life cycle, beyond 5' end protection. Overall, our results support a model in which miR-122 stabilizes the HCV genome by shielding its 5' terminus from cellular pyrophosphatase activity and subsequent turnover by exonucleases (Xrn1/2).
Figures






References
-
- Jopling C.L. Regulation of Hepatitis C virus by microRNA-122. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008; 36:1220–1223. - PubMed
-
- Jopling C.L., Yi M., Lancaster A.M., Lemon S.M., Sarnow P.. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific microRNA. Science. 2005; 309:1577–1581. - PubMed
-
- Janssen H.L., Reesink H.W., Lawitz E.J., Zeuzem S., Rodriguez-Torres M., Patel K., van der Meer A.J., Patick A.K., Chen A., Zhou Y. et al. . Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013; 368:1685–1694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

