Overexpression of Contactin 1 promotes growth, migration and invasion in Hs578T breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29673312
- PMCID: PMC5907708
- DOI: 10.1186/s12860-018-0154-3
Overexpression of Contactin 1 promotes growth, migration and invasion in Hs578T breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Contactin1 (CNTN1) has been shown to play an important role in the invasion and metastasis of several tumors; however, the role of CNTN1 in breast cancer has not been fully studied. The purpose of this study is to investigate the role of CNTN1 in regulating tumor growth, migration and invasion in breast cancer.
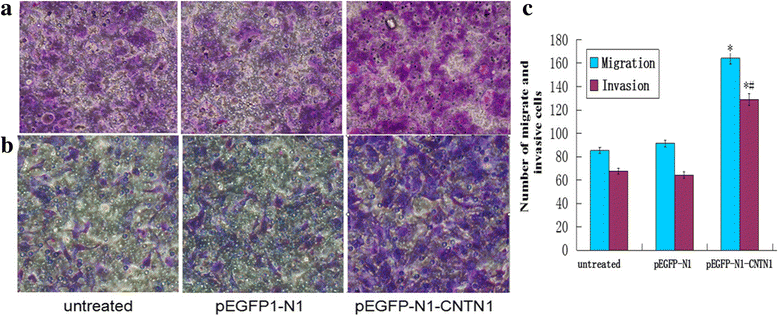
Results: To investigate its function, CNTN1 was expressed in Hs578T cells. CNTN1 expression was confirmed by western blot, immunohistochemistry and real-time RT-PCR. The effect of CNTN1 overexpression on proliferation, migration and invasion of Hs578T breast cancer cells was assessed in vitro and in vivo. Our results showed that CNTN1 overexpression promoted Hs578T cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, colony formation, invasion and migration. Notably, overexpression of CNTN1 in Hs578T cells enhanced the growth of mouse xenograft tumors.
Conclusions: CNTN1 promotes growth, metastasis and invasion of Hs578T breast cancer cell line. Thus, therapies targeting CNTN1 may prove efficacious for breast cancer. However, further investigation is required to understand the mechanism by which CNTN1 influences proliferation, metastasis and invasion in breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CNTN1; Hs578T; Invasion; Migration; Proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal studies were performed in accordance with Guidelines of the Animal Care. All animal procedures complied with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were performed after approval by the Committee of Animal Experimentation (Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China). This study does not involve the use of human data or tissue.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neural Cell Adhesion Protein CNTN1 Promotes the Metastatic Progression of Prostate Cancer.Cancer Res. 2016 Mar 15;76(6):1603-14. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1898. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26795349
-
Contactin 1 as a potential biomarker promotes cell proliferation and invasion in thyroid cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):12473-81. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26722434 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-409-3p regulates cell invasion and metastasis by targeting ZEB1 in breast cancer.IUBMB Life. 2016 May;68(5):394-402. doi: 10.1002/iub.1494. Epub 2016 Apr 15. IUBMB Life. 2016. PMID: 27079864
-
Contactin 1: An Important and Emerging Oncogenic Protein Promoting Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 31;11(8):874. doi: 10.3390/genes11080874. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32752094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contactin 1: A potential therapeutic target and biomarker in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 7;21(33):9707-16. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9707. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26361417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Co-pathogenic Target Gene CNTN1 Involved in Coronary Artery Disease and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Has Potential for Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease.Anatol J Cardiol. 2024 Aug;28(8):381-392. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2024.4331. Anatol J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39087405 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted RASSF1A expression inhibits proliferation of HER2‑positive breast cancer cells in vitro.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Apr 11;25(6):245. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11944. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37153885 Free PMC article.
-
Lentivirus-mediated silencing of CNTN1 enhances gefitinib sensitivity by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jun;21(6):433. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12694. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33868471 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Landscape and Immune Microenvironment Features of Preinvasive and Early Invasive Lung Adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Oncol. 2019 Nov;14(11):1912-1923. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.07.031. Epub 2019 Aug 22. J Thorac Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31446140 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis based on IFN-γ and SASP related genes, bulk RNA and single-cell sequencing to evaluate the prognosis and immune landscape of stomach adenocarcinoma.Genes Genomics. 2025 Jun;47(6):777-796. doi: 10.1007/s13258-025-01646-7. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Genes Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40293675
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Breast Cancer Statistics. [October 10, 2012]. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/statistics/
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Screening for Breast Cancer. [June 4, 2013]. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/cancer/breast/basic_info/screening.htm.
-
- SEER Statistics Fact Sheets: Breast Cancer. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; [March 15, 2015]. Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

