Celecoxib exerts protective effects in the vascular endothelium via COX-2-independent activation of AMPK-CREB-Nrf2 signalling
- PMID: 29674687
- PMCID: PMC5908847
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24548-z
Celecoxib exerts protective effects in the vascular endothelium via COX-2-independent activation of AMPK-CREB-Nrf2 signalling
Abstract
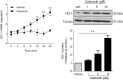
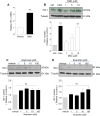
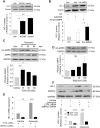
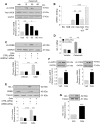
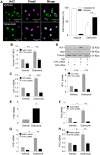
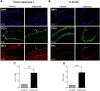
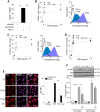
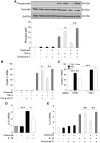
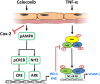
Although concern remains about the athero-thrombotic risk posed by cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-2-selective inhibitors, recent data implicates rofecoxib, while celecoxib appears equivalent to NSAIDs naproxen and ibuprofen. We investigated the hypothesis that celecoxib activates AMP kinase (AMPK) signalling to enhance vascular endothelial protection. In human arterial and venous endothelial cells (EC), and in contrast to ibuprofen and naproxen, celecoxib induced the protective protein heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). Celecoxib derivative 2,5-dimethyl-celecoxib (DMC) which lacks COX-2 inhibition also upregulated HO-1, implicating a COX-2-independent mechanism. Celecoxib activated AMPKα(Thr172) and CREB-1(Ser133) phosphorylation leading to Nrf2 nuclear translocation. Importantly, these responses were not reproduced by ibuprofen or naproxen, while AMPKα silencing abrogated celecoxib-mediated CREB and Nrf2 activation. Moreover, celecoxib induced H-ferritin via the same pathway, and increased HO-1 and H-ferritin in the aortic endothelium of mice fed celecoxib (1000 ppm) or control chow. Functionally, celecoxib inhibited TNF-α-induced NF-κB p65(Ser536) phosphorylation by activating AMPK. This attenuated VCAM-1 upregulation via induction of HO-1, a response reproduced by DMC but not ibuprofen or naproxen. Similarly, celecoxib prevented IL-1β-mediated induction of IL-6. Celecoxib enhances vascular protection via AMPK-CREB-Nrf2 signalling, a mechanism which may mitigate cardiovascular risk in patients prescribed celecoxib. Understanding NSAID heterogeneity and COX-2-independent signalling will ultimately lead to safer anti-inflammatory drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PKCε-CREB-Nrf2 signalling induces HO-1 in the vascular endothelium and enhances resistance to inflammation and apoptosis.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Jun 1;106(3):509-19. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv131. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25883219 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate-mediated activation of an AMPK-CREB-dependent pathway: a novel mechanism for vascular protection in chronic systemic inflammation.Ann Rheum Dis. 2016 Feb;75(2):439-48. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206305. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 25575725 Free PMC article.
-
Celecoxib activates PI-3K/Akt and mitochondrial redox signaling to enhance heme oxygenase-1-mediated anti-inflammatory activity in vascular endothelium.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Apr 15;48(8):1013-23. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.01.017. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20083195
-
Docosahexaenoic acid inhibition of inflammation is partially via cross-talk between Nrf2/heme oxygenase 1 and IKK/NF-κB pathways.J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Jan;24(1):204-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 Aug 15. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 22901690
-
Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling: An important molecular mechanism of herbal medicine in the treatment of atherosclerosis via the protection of vascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul 6;34:43-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.023. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35024180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective effects of melatonin and celecoxib against ethanol-induced neurodegeneration: a computational and pharmacological approach.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Aug 2;13:2715-2727. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S207310. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31447548 Free PMC article.
-
Flurbiprofen axetil alleviates the effect of formalin-induced inflammatory pain on the cognitive function of rats with mild cognitive impairment through the AMPKα/NF-κB signaling pathway.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Nov;10(22):1210. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-4997. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36544641 Free PMC article.
-
Observational study of people infected with SARS-Cov-2, treated with amantadine.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Dec;72(6):1538-1541. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00168-1. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33040252 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cell migration and invasion in human colorectal carcinoma HCT-116 cells through down-regulation of prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4.BMB Rep. 2018 Oct;51(10):532-537. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.10.120. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 30269738 Free PMC article.
-
Solution Blow Spun Mats with Beaded-Fiber Morphologies as a Drug Delivery System with Potential Use for Skin Wound Dressing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Apr 23;17(16):23466-23483. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c16675. Epub 2025 Apr 10. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40208007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists’ Collaboration. Bhala N, et al. Vascular and upper gastrointestinal effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: meta-analyses of individual participant data from randomised trials. Lancet. 2013;382:769–779. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60900-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

