Good function and high patient satisfaction at mean 2.8 years after dual mobility THA following femoral neck fracture: a cross-sectional study of 124 patients
- PMID: 29674847
- PMCID: PMC5898881
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S157671
Good function and high patient satisfaction at mean 2.8 years after dual mobility THA following femoral neck fracture: a cross-sectional study of 124 patients
Abstract
Aims: Our aim was to investigate function, health status and satisfaction in patients treated with primary dual mobility (DM) total hip arthroplasty (THA) after displaced femoral neck fracture (FNF).
Patients and methods: From 2005-2011, 414 consecutive FNF patients received Saturne DM THA. At a minimum of 1-year follow-up, 124 (95 women) were evaluated with Oxford Hip Score (OHS), Harris Hip Score (HHS), health-related quality of life (HRQoL) measure (EQ-5D) and two functional tests: Timed Up and Go (TUG) and Sit to Stand 10 times (STS). The FNF patients were matched 1:2 by age, sex and surgery date with patients receiving THA due to osteoarthrosis (OA group) and 1-year OHS and EQ5D were compared. FNF patients were matched by age and sex with the general population index (GPI) for EQ-5D comparison.
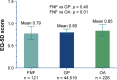
Results: Patient age at surgery after FNF was mean 74.8 (range 30-92) years. At mean follow-up of 2.8 (range 1.0-7.7) years, mean EQ-5D score was 0.79 (SD 0.15) in the FNF group, which was similar to the matched GPI (p = 0.4), but lower (p = 0.014) compared to the OA group. Mean OHS was 36.4 (SD 9.5) in the FNF group and 38.4 (SD 7.2) in the OA group (p = 0.18). HHS in the FNF group was 78.7 (SD 15.5). Mean TUG time was 13.5 (SD 4.9) secs, and mean STS was 37.9 (SD 15.3) secs. Eighty nine percent (n = 111) of FNF patients were satisfied with the operation result.
Conclusion: DM THA following displaced FNF provides a good functional result and quality of life in addition to high patient satisfaction.
Keywords: EQ-5D; Oxford Hip Score; dual mobility cup; femoral neck fracture; hip arthroplasty; patient reported outcome measures.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Good functional outcome but not regained health related quality of life in the majority of 20-69 years old patients with femoral neck fracture treated with internal fixation: A prospective 2-year follow-up study of 182 patients.Injury. 2017 Dec;48(12):2744-2753. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2017.10.028. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Injury. 2017. PMID: 29106948
-
Low dislocation rate of Saturne®/Avantage® dual-mobility THA after displaced femoral neck fracture: a cohort study of 966 hips with a minimum 1.6-year follow-up.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019 May;139(5):605-612. doi: 10.1007/s00402-018-3093-8. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019. PMID: 30547264
-
Total Hip Arthroplasty Leads to Better Results After Low-Energy Displaced Femoral Neck Fracture in Patients Aged 55 to 70 Years: A Randomized Controlled Multicenter Trial Comparing Internal Fixation and Total Hip Arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022 Aug 3;104(15):1341-1351. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.21.01411. Epub 2022 May 31. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022. PMID: 35700073 Clinical Trial.
-
Outcomes of dual-mobility total hip arthroplasty versus bipolar hemiarthroplasty for patients with femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Feb 24;16(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02316-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 33627151 Free PMC article.
-
Total Hip Arthroplasty in fracture neck of femur: A review of the literature.Acta Orthop Belg. 2023 Mar;89(1):29-36. doi: 10.52628/89.1.8497. Acta Orthop Belg. 2023. PMID: 37294982 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors and modes of failure in the modern dual mobility implant. A systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Jun 14;22(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04404-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34126990 Free PMC article.
-
Hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty in 30,830 patients with hip fractures: data from the Dutch Arthroplasty Register on revision and risk factors for revision.Acta Orthop. 2018 Oct;89(5):509-514. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2018.1499069. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Acta Orthop. 2018. PMID: 30080985 Free PMC article.
-
Dual mobility in primary total hip arthroplasty: current concepts.EFORT Open Rev. 2019 Nov 8;4(11):640-646. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.4.180089. eCollection 2019 Nov. EFORT Open Rev. 2019. PMID: 31754471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do Dual-mobility Cups Reduce Revision Risk in Femoral Neck Fractures Compared With Conventional THA Designs? An International Meta-analysis of Arthroplasty Registries.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022 Oct 1;480(10):1912-1925. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002275. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2022. PMID: 35767813 Free PMC article.
-
The majority of community-dwelling hip fracture patients return to independent living with minor increase in care needs: a prospective cohort study.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 May;143(5):2475-2484. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04472-8. Epub 2022 May 20. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 35596021
References
-
- Hopley C, Stengel D, Ekkernkamp A, Wich M. Primary total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced intracapsular hip fractures in older patients: systematic review. BMJ. 2010;340:c2332. - PubMed
-
- Johansson T. Internal fixation compared with total hip replacement for displaced femoral neck fractures: a minimum fifteen-year follow-up study of a previously reported randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(6):e46. - PubMed
-
- Adam P, Philippe R, Ehlinger M, et al. Dual mobility cups hip arthroplasty as a treatment for displaced fracture of the femoral neck in the elderly. A prospective, systematic, multicenter study with specific focus on postoperative dislocation. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98(3):296–300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical