Effect of dietary oils on peripheral neuropathy-related endpoints in dietary obese rats
- PMID: 29674850
- PMCID: PMC5898889
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S159071
Effect of dietary oils on peripheral neuropathy-related endpoints in dietary obese rats
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to determine the effect of dietary oils (olive, safflower, evening primrose, flaxseed, or menhaden) enriched in different mono unsaturated fatty acids or polyunsaturated fatty acids on peripheral neuropathies in diet-induced obese Sprague-Dawley rats.
Materials and methods: Rats at 12 weeks of age were fed a high-fat diet (45% kcal) for 16 weeks. Afterward, the rats were fed diets with 50% of the kilocalories of fat derived from lard replaced by the different dietary oils. In addition, a control group fed a standard diet (4% kcal fat) and a high fat fed group (45% kcal) were maintained. The treatment period was 32 weeks. The endpoints evaluated included motor and sensory nerve conduction velocity, thermal sensitivity, innervation of sensory nerves in the cornea and skin, and vascular relaxation by epineurial arterioles.
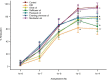
Results: Menhaden oil provided the greatest benefit for improving peripheral nerve damage caused by dietary obesity. Similar results were obtained when we examined acetylcholine-mediated vascular relaxation of epineurial arterioles of the sciatic nerve. Enriching the diets with fatty acids derived from the other oils provided minimal to partial improvements.
Conclusion: These studies suggest that omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids derived from fish oil could be an effective treatment for neural and vascular complications associated with obesity.
Keywords: fish oil; nerve conduction velocity; omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids; peripheral neuropathy; vascular reactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Cortez M, Singleton JR, Smith AG. Glucose intolerance, metabolic syndrome, and neuropathy. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;126:109–122. - PubMed
-
- Yorek MA. Is fish oil a potential treatment for diabetic peripheral neuropathy? Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Vincent AM, Callaghan BC, Smith AL, Feldman EL. Diabetic neuropathy: cellular mechanisms as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7:573–583. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

