Expansion of the (BB) 〉metallacycle with coinage metal cations: formation of B-M-Ru-B (M = Cu, Ag, Au) dimetalacyclodiboryls
- PMID: 29675252
- PMCID: PMC5892348
- DOI: 10.1039/c8sc00190a
Expansion of the (BB) 〉metallacycle with coinage metal cations: formation of B-M-Ru-B (M = Cu, Ag, Au) dimetalacyclodiboryls
Abstract
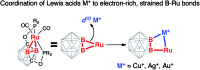
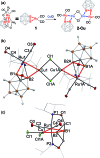
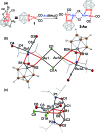
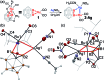
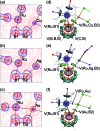
In this work, we introduce a novel approach for the selective assembly of heterometallic complexes by unprecedented coordination of coinage metal cations to strained single ruthenium-boron bonds on a surface of icosahedral boron clusters. M(i) cations (M = Cu, Ag, and Au) insert into B-Ru bonds of the (BB)-carboryne complex of ruthenium with the formation of four-membered B-M-Ru-B metalacycles. Results of theoretical calculations suggest that bonding within these metalacycles can be best described as unusual three-center-two-electron B-M···Ru interactions that are isolobal to B-H···Ru borane coordination for M = Cu and Ag, or the pairs of two-center-two electron B-Au and Au-Ru interactions for M = Au. These transformations comprise the first synthetic route to exohedral coinage metal boryl complexes of icosahedral closo-{C2B10} clusters, which feature short Cu-B (2.029(2) Å) and Ag-B (2.182(3) Å) bonds and the shortest Au-B bond (2.027(2) Å) reported to date. The reported heterometallic complexes contain Cu(i) and Au(i) centers in uncharacteristic square-planar coordination environments. These findings pave the way to rational construction of a broader class of multimetallic architectures featuring M-B bonds.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

