Anterior and posterior capsule densitometry levels after femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery
- PMID: 29675381
- PMCID: PMC5902367
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2018.04.14
Anterior and posterior capsule densitometry levels after femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery
Abstract
Aim: To analyze and compare five different variables over one year follow-up (1wk, 1, 3, 6 and 12mo): anterior capsule (AC), and posterior capsule (PC) area densitometry values, AC and PC linear densitometry values, and AC opening area reduction ratio after femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery.
Methods: This was a prospective comparative study. Seventy-one patients underwent femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery on single eye between June 2014 and December 2015. A 5.0 mm diameter laser assisted anterior capsulotomy was performed on all eyes. In every post-surgery evaluation, AC opacificaction (ACO) and PC opacification (PCO) density levels were provided by Oculus Pentacam®HR using area and linear densitometry methods. Digital images were captured with a slit-lamp Topcon photographic camera and IMAGEnet® 5 software. The AC opening area on the digital images was measured using the Sketchandcalc area calculator and converted to reduction ratio levels.
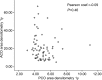
Results: Using Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC), we found no correlation (r=-0.091, P=0.46) in the twelfth month assessment between the evolution of ACO area densitometry values and PCO area densitometry values considered as independent variables. We found no correlation, using PCC (r=-0.096, P=0.43) between the evolution of ACO linear densitometry values and PCO linear densitometry values, in the twelfth month visit, working both as independent variables. AC linear densitometry levels and AC area densitometry levels continued to grow strongly from sixth to twelfth months. Analysis of the values of AC opening area reduction ratio (1wk, 1, 3, 6, 12mo) revealed statistically significant differences between the values of successive examinations but the magnitude of the change decreased. In the final period of monitoring between six and twelve months the magnitude of change was low.
Conclusion: Our results show strong increases of Scheimpflug ACO densitometry values from the sixth to the twelfth month while capsulorhexis area reduction ratio levels displayed a considerable decrease. We found no correlation between ACO area and linear densitometry values and PCO area and linear densitometry values, in the twelfth month examination, working as independent variables.
Keywords: Pentacam®HR Scheimpflug; anterior capsule opacification; area densitometry; femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery; linear densitometry; posterior capsule pacification.
Figures


References
-
- Werner L, Pandey SK, Escobar-Gomez M, Visessook N, Peng Q, Apple DJ. Anterior capsule opacification: A histological study comparing different IOL styles. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:463–467. - PubMed
-
- Werner L, Pandey SK, Apple DJ, Escobar-Gomez M, McLendon L, Macky TA. Anterior capsule opacification: correlation of pathologic findings with clinical sequelae. Ophthalmology. 2001;108(9):1675–1681. - PubMed
-
- Vasavada AR, Raj SM, Shah GD, Nanavaty MA. Posterior capsule opacification after lens implantation. Expert Rev Ophthalmol. 2013;8(2):141–149.
-
- Minami K, Honbo M, Mori Y, Kataoka Y, Miyata K. Area densitometry using rotating Scheimpflug photography for posterior capsule opacification and surface light scattering analyses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015;41:2444–2449. - PubMed
-
- Sacu S, Findl O, Menapace R, Georgopoulos M, Buehl W, Rainer G. Assessment of anterior capsule opacification: photographic technique and quantification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28(2):271–275. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
