Unmet healthcare needs of elderly people in Korea
- PMID: 29678164
- PMCID: PMC5910628
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-018-0786-3
Unmet healthcare needs of elderly people in Korea
Abstract
Background: Elderly people often have more complicated healthcare needs than younger adults due to additional functional decline, physical illness, and psychosocial needs. Unmet healthcare needs increase illness severity, complications, and mortality. Despite this, research on the unmet healthcare needs of elderly people is limited in Korea. This study analysed the effect of functional deterioration related to aging on unmet healthcare needs based on the Korea Health Panel Study.
Methods: This cross-sectional study used data from the 2011-2013 survey of 8666 baseline participants aged 65 years and older. Unmet healthcare needs were calculated using a complex weighted sample design. Group differences in categorical variables were analysed using the Rao-Scott Chi-square test. Using logistic regression analysis, the association between unmet healthcare needs and aging factors was analysed.
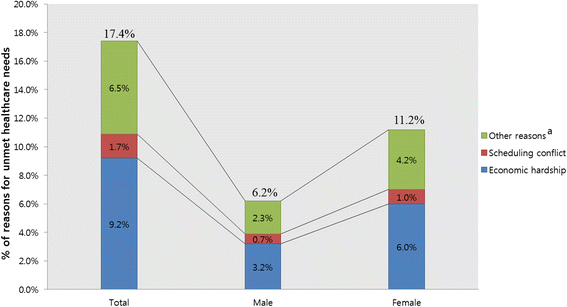
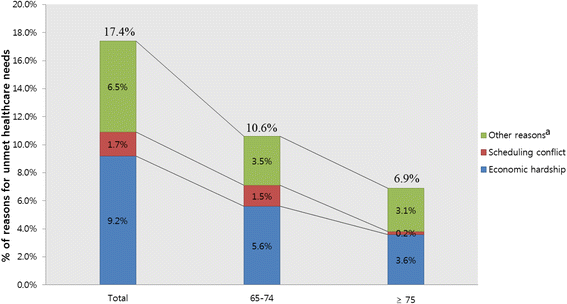
Results: The prevalence of unmet healthcare needs in Korean elderly was 17.4%. Among them, the leading reason was economic hardship (9.2%). Adjusting for sex, age, socioeconomic characteristics, and health-related characteristics, the group with depression syndrome was 1.45 times more likely to have unmet healthcare needs than that without depression syndrome (95% CI = 1.13-1.88). The group with visual impairment was 1.48 times more likely to have unmet healthcare needs than that without it (95% CI = 1.22-1.79). The group with hearing impairment was 1.40 times more likely to have unmet healthcare needs than that without it (95% CI = 1.15-1.72). The group with memory impairment was 1.74 times more likely to have unmet healthcare needs than that without it (95% CI = 1.28-2.36).
Conclusions: The unmet medical needs of the elderly are more diverse than those of younger adults. This is because not only socioeconomic and health-related factors but also aging factors that are important to the health of the elderly are included. All factors were linked organically; therefore, integrated care is needed to improve healthcare among the elderly. To resolve these unmet healthcare needs, it is necessary to reorganize the healthcare system in Korea to include preventive and rehabilitative services that address chronic diseases in an aged society and promote life-long health promotion.
Keywords: Aging; Elderly; Unmet healthcare needs.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable. This survey did not need formal ethics approval as stated by national laws (Article 17 of the Statistics Act). We used only public data from the KHPS, which did not include any personal identification. The Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs provided the data and permission to use and analyse it.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors affecting unmet healthcare needs of older people in Korea.Int Nurs Rev. 2013 Dec;60(4):510-9. doi: 10.1111/inr.12055. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Int Nurs Rev. 2013. PMID: 24251942
-
Association Between Convenience of Transportation and Unmet Healthcare Needs of Rural Elderly in Korea.J Prev Med Public Health. 2019 Nov;52(6):355-365. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.19.172. Epub 2019 Oct 3. J Prev Med Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31795612 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a sexual difference in the relationship between sociodemographic information and the unmet dental care needs of disabled adults? An analysis from a national survey on persons with disabilities.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Nov 3;23(1):830. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03576-w. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37924058 Free PMC article.
-
Changing factors and changing needs in women's health care.Nurs Clin North Am. 1986 Mar;21(1):111-23. Nurs Clin North Am. 1986. PMID: 3513129 Review.
-
Development of a senior-specific, citizen-oriented healthcare service system in South Korea based on the Canadian 48/6 model of care.BMC Geriatr. 2020 Jan 31;20(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1397-3. BMC Geriatr. 2020. PMID: 32005155 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Dental Prosthetic Treatment in Patients with Cancer Aged 65 Years and Older after Expanded Health Insurance Coverage: A Retrospective Clinical Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Sep 16;60(9):1509. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091509. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336550 Free PMC article.
-
Why not see a doctor when ill? Evidence from the Chinese elderly.BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 Jun 10;19(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4212-0. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019. PMID: 31182079 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data.BMC Public Health. 2023 May 23;23(1):928. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15763-z. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37221526 Free PMC article.
-
Using an Extended Technology Acceptance Model to Understand the Factors Influencing Telehealth Utilization After Flattening the COVID-19 Curve in South Korea: Cross-sectional Survey Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2021 Jan 8;9(1):e25435. doi: 10.2196/25435. JMIR Med Inform. 2021. PMID: 33395397 Free PMC article.
-
Towards universal health coverage in the context of population ageing: a narrative review on the implications from the long-term care system in Japan.Arch Public Health. 2022 Sep 21;80(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s13690-022-00970-8. Arch Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36131300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J, Hou F. Unmet needs for health care. Health Rep. 2002;13(2):23–34. - PubMed
-
- OECD. Health at a Glance 2015: OECD Indicators. OECD Publishing; 2015. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/health_glance-2015-40-en.pdf?exp.... Accessed 15 June 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

