Prescription Medication Use Among Community-Based U.S. Adults With Chronic Low Back Pain: A Cross-Sectional Population Based Study
- PMID: 29678564
- PMCID: PMC6163076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpain.2018.04.004
Prescription Medication Use Among Community-Based U.S. Adults With Chronic Low Back Pain: A Cross-Sectional Population Based Study
Abstract
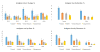
Many classes of medications have been evaluated in chronic low back pain (cLBP), however their utilization in the community remains unclear. We examined patterns of prescription medication use among Americans with cLBP in a nationally representative, community-based sample. The Back Pain Survey was administered to a representative sample of U.S. adults aged 20 to 69 years (N = 5,103) during the 2009 to 2010 cycle of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. cLBP was defined as self-reported pain in the area between the lower posterior margin of the ribcage and the horizontal gluteal fold on most days for at least 3 months (N = 700). Home-based interviews with pill bottle verification were used to capture commonly prescribed medications for chronic pain. Among the sample of U.S. adults with cLBP aged 20 to 69 years, 36.9% took at least 1 prescription pain medication in the past 30 days; of them, 18.8% used opioids, 9.7% nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, 8.5% muscle relaxants, and 6.9% gabapentin or pregabalin. Nonpain antidepressants and hypnotics were used by 17.8% and 4.7%, respectively. Opioids were used long-term in 76.9% of cases (median = 2 years) and were frequently coadministered with antidepressants, benzodiazepines, or hypnotics. Ninety-four percent of prescription opioids in the cLBP population were used by individuals with less than a college education. Opioids were the most widely used prescription analgesic class in community-based U.S. adults with cLBP and were often coadministered with other central nervous system-active medications. Opioid use was highly prevalent among less educated Americans with cLBP.
Perspective: Because prescription opioid use is an issue of national concern, we examined pain-related prescription medication use in community-dwelling U.S. adults with cLBP. Opioids were the most common prescription pain medication, typically used long-term, in combination with other central nervous system-active agents, and disproportionately among individuals with less than a college education.
Keywords: Low back pain; analgesics; epidemiology; opioids.
Copyright © 2018 The American Pain Society. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Berthelot J-M, Darrieutort-Lafitte C, Le Goff B, Maugars Y. Strong opioids for noncancer pain due to musculoskeletal diseases: Not more effective than acetaminophen or NSAIDs. Joint Bone Spine. 2015;82:397–401. - PubMed
-
- Chelminski PR, Ives TJ, Felix KM, Prakken SD, Miller TM, Perhac JS, Malone RM, Bryant ME, DeWalt DA, Pignone MP. A primary care, multi-disciplinary disease management program for opioid-treated patients with chronic non-cancer pain and a high burden of psychiatric comorbidity. BMC Health Serv Res. 2005;5:3. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chou R, Qaseem A, Snow V, Casey D, Cross JT, Shekelle P, Owens DK Clinical Efficacy Assessment Subcommittee of the American College of Physicians, American College of Physicians, American Pain Society Low Back Pain Guidelines Panel. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain: a joint clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:478–91. - PubMed
-
- Chou R, Turner JA, Devine EB, Hansen RN, Sullivan SD, Blazina I, Dana T, Bougatsos C, Deyo RA. The effectiveness and risks of long-term opioid therapy for chronic pain: a systematic review for a National Institutes of Health Pathways to Prevention Workshop. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:276–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

