Draft genome sequence of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis provides insights into the evolution of the tea genome and tea quality
- PMID: 29678829
- PMCID: PMC5939082
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1719622115
Draft genome sequence of Camellia sinensis var. sinensis provides insights into the evolution of the tea genome and tea quality
Abstract
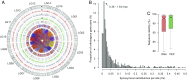
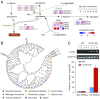
Tea, one of the world's most important beverage crops, provides numerous secondary metabolites that account for its rich taste and health benefits. Here we present a high-quality sequence of the genome of tea, Camellia sinensis var. sinensis (CSS), using both Illumina and PacBio sequencing technologies. At least 64% of the 3.1-Gb genome assembly consists of repetitive sequences, and the rest yields 33,932 high-confidence predictions of encoded proteins. Divergence between two major lineages, CSS and Camellia sinensis var. assamica (CSA), is calculated to ∼0.38 to 1.54 million years ago (Mya). Analysis of genic collinearity reveals that the tea genome is the product of two rounds of whole-genome duplications (WGDs) that occurred ∼30 to 40 and ∼90 to 100 Mya. We provide evidence that these WGD events, and subsequent paralogous duplications, had major impacts on the copy numbers of secondary metabolite genes, particularly genes critical to producing three key quality compounds: catechins, theanine, and caffeine. Analyses of transcriptome and phytochemistry data show that amplification and transcriptional divergence of genes encoding a large acyltransferase family and leucoanthocyanidin reductases are associated with the characteristic young leaf accumulation of monomeric galloylated catechins in tea, while functional divergence of a single member of the glutamine synthetase gene family yielded theanine synthetase. This genome sequence will facilitate understanding of tea genome evolution and tea metabolite pathways, and will promote germplasm utilization for breeding improved tea varieties.
Keywords: catechins biosynthesis; comparative genomics; genome evolution; tea quality; theanine biosynthesis.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wheeler DS, Wheeler WJ. The medicinal chemistry of tea. Drug Dev Res. 2004;61:45–65.
-
- Yang CS, Hong J. Prevention of chronic diseases by tea: Possible mechanisms and human relevance. Annu Rev Nutr. 2013;33:161–181. - PubMed
-
- Kingdom-Ward F. Does wild tea exist? Nature. 1950;165:297–299.
-
- Taniguchi F, et al. Worldwide core collections of tea (Camellia sinensis) based on SSR markers. Tree Genet Genomes. 2014;10:1555–1565.
-
- Kaundun SS, Matsumoto S. Development of CAPS markers based on three key genes of the phenylpropanoid pathway in tea, Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze, and differentiation between assamica and sinensis varieties. Theor Appl Genet. 2003;106:375–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

