Extracellular vesicles and their content in bioactive lipid mediators: more than a sack of microRNA
- PMID: 29678959
- PMCID: PMC6210911
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.R084640
Extracellular vesicles and their content in bioactive lipid mediators: more than a sack of microRNA
Abstract
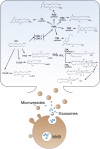
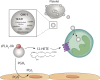
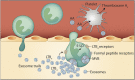
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), such as exosomes and microvesicles, are small membrane-bound vesicles released by cells under various conditions. In a multitude of physiological and pathological conditions, EVs contribute to intercellular communication by facilitating exchange of material between cells. Rapidly growing interest is aimed at better understanding EV function and their use as biomarkers. The vast EV cargo includes cytokines, growth factors, organelles, nucleic acids (messenger and micro RNA), and transcription factors. A large proportion of research dedicated to EVs is focused on their microRNA cargo; however, much less is known about other EV constituents, in particular, eicosanoids. These potent bioactive lipid mediators, derived from arachidonic acid, are shuttled in EVs along with the enzymes in charge of their synthesis. In the extracellular milieu, EVs also interact with secreted phospholipases to generate eicosanoids, which then regulate the transfer of cargo into a cellular recipient. Eicosanoids are useful as biomarkers and contribute to a variety of biological functions, including modulation of distal immune responses. Here, we review the reported roles of eicosanoids conveyed by EVs and describe their potential as biomarkers.
Keywords: cancer; eicosanoids; exosomes; microvesicles; neutrophils; platelets.
Copyright © 2018 Boilard.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Ridger V. C., Boulanger C. M., Angelillo-Scherrer A., Badimon L., Blanc-Brude O., Bochaton-Piallat M. L., Boilard E., Buzas E. I., Caporali A., Dignat-George F., et al. 2017. Microvesicles in vascular homeostasis and diseases. Position Paper of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Working Group on Atherosclerosis and Vascular Biology. Thromb. Haemost. 117: 1296–1316. - PubMed
-
- Colombo M., Raposo G., and Thery C.. 2014. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 30: 255–289. - PubMed
-
- Record M., Subra C., Silvente-Poirot S., and Poirot M.. 2011. Exosomes as intercellular signalosomes and pharmacological effectors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 81: 1171–1182. - PubMed
-
- Jimenez A. J., Maiuri P., Lafaurie-Janvore J., Divoux S., Piel M., and Perez F.. 2014. ESCRT machinery is required for plasma membrane repair. Science. 343: 1247136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

