Health-related quality of life in Asian patients with breast cancer: a systematic review
- PMID: 29678980
- PMCID: PMC5914715
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020512
Health-related quality of life in Asian patients with breast cancer: a systematic review
Abstract
Objective: To summarise the evidence on determinants of health-related quality of life (HRQL) in Asian patients with breast cancer.
Design: Systematic review conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations and registered with PROSPERO (CRD42015032468).
Methods: According to the PRISMA guidelines, databases of MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase and PsycINFO were systematically searched using the following terms and synonyms: breast cancer, quality of life and Asia. Articles reporting on HRQL using EORTC-QLQ-C30, EORTC-QLQ-BR23, FACT-G and FACT-B questionnaires in Asian patients with breast cancer were eligible for inclusion. The methodological quality of each article was assessed using the quality assessment scale for cross-sectional studies or the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale for cohort studies.
Results: Fifty-seven articles were selected for this qualitative synthesis, of which 43 (75%) were cross-sectional and 14 (25%) were longitudinal studies. Over 75 different determinants of HRQL were studied with either the EORTC or FACT questionnaires. Patients with comorbidities, treated with chemotherapy, with less social support and with more unmet needs have poorer HRQL. HRQL improves over time. Discordant results in studies were found in the association of age, marital status, household income, type of surgery, radiotherapy and hormone therapy and unmet sexuality needs with poor global health status or overall well-being.
Conclusions: In Asia, patients with breast cancer, in particular those with other comorbidities and those treated with chemotherapy, with less social support and with more unmet needs, have poorer HRQL. Appropriate social support and meeting the needs of patients may improve patients' HRQL.
Keywords: breast cancer; health-related quality of life; patient-reported outcomes.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
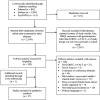
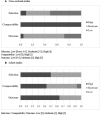
References
-
- Mousavi-Jarrrahi SH, Kasaeian A, Mansori K, et al. Addressing the younger age at onset in breast cancer patients in Asia: an age-period-cohort analysis of fifty years of quality data from the international agency for research on cancer. ISRN Oncol 2013;2013:1–8. 10.1155/2013/429862 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
