Proteome-wide analysis of cysteine oxidation reveals metabolic sensitivity to redox stress
- PMID: 29679077
- PMCID: PMC5910380
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04003-3
Proteome-wide analysis of cysteine oxidation reveals metabolic sensitivity to redox stress
Abstract
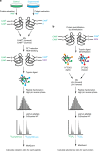
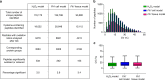
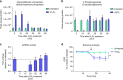
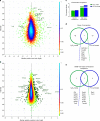
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are increasingly recognised as important signalling molecules through oxidation of protein cysteine residues. Comprehensive identification of redox-regulated proteins and pathways is crucial to understand ROS-mediated events. Here, we present stable isotope cysteine labelling with iodoacetamide (SICyLIA), a mass spectrometry-based workflow to assess proteome-scale cysteine oxidation. SICyLIA does not require enrichment steps and achieves unbiased proteome-wide sensitivity. Applying SICyLIA to diverse cellular models and primary tissues provides detailed insights into thiol oxidation proteomes. Our results demonstrate that acute and chronic oxidative stress causes oxidation of distinct metabolic proteins, indicating that cysteine oxidation plays a key role in the metabolic adaptation to redox stress. Analysis of mouse kidneys identifies oxidation of proteins circulating in biofluids, through which cellular redox stress can affect whole-body physiology. Obtaining accurate peptide oxidation profiles from complex organs using SICyLIA holds promise for future analysis of patient-derived samples to study human pathologies.
Conflict of interest statement
E.G. is a Shareholder and Director at MetaboMed Ltd, Israel. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Szatrowski TP, Nathan CF. Production of large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1991;51:794–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

