Randomized, controlled study of bleselumab (ASKP1240) pharmacokinetics and safety in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis
- PMID: 29679478
- PMCID: PMC6032846
- DOI: 10.1002/bdd.2130
Randomized, controlled study of bleselumab (ASKP1240) pharmacokinetics and safety in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis
Abstract
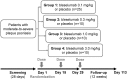
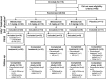
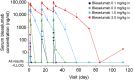
This study evaluated the pharmacokinetics (PK), efficacy, safety, and tolerability of bleselumab - a fully-human anti-CD40 monoclonal recombinant IgG4. Patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis were randomized on day 1 to receive bleselumab or placebo on days 1, 15 and 29 in a dose-escalation of bleselumab at 0.1, 0.3, 1.0 or 3.0 mg/kg. The safety-analysis set (SAF) and full-analysis set (FAS) included all patients who received bleselumab or placebo, and the PK-analysis set (PKAS) included patients in the SAF with ≥1 quantifiable serum bleselumab concentration. Serial blood samples were collected after each dose, and the bleselumab serum concentration was measured. After each dose, the area-under-the-concentration-time curve over 336 hours (AUC336 ) and the maximum serum concentration (Cmax ), and dose proportionality of AUC336 and Cmax were determined. The psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score, the physician static global assessment (PSGA) score, the percentage body surface area (%BSA) affected with psoriasis, adverse events and laboratory parameters were assessed. Sixty patients were randomized and included in the SAF/FAS (bleselumab, n = 49; placebo, n = 11); 48 formed the PKAS. Bleselumab Cmax and AUC336 were more than dose proportional in the range 0.1-3.0 mg/kg, suggesting nonlinear PK after single/multiple doses. No clinically significant infusion reactions, cytokine-release syndrome, or thromboembolic events were reported. Bleselumab did not improve the PASI scores, PSGA scores, or %BSA versus placebo. Transient elevation of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase levels by >3 × upper limit of normal were observed in four (8.2%) and two (4.1%) patients, respectively, in the 1.0 or 3.0 mg/kg groups. Patients with liver function test increases had no concurrent changes in bilirubin. Bleselumab demonstrated nonlinear PK after single and multiple doses, with few adverse reactions.
Keywords: bleselumab; moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis; pharmacokinetics; randomized controlled trial.
© 2018 The Authors Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized, phase 1b study of the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, and tolerability of bleselumab, a fully human, anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody, in kidney transplantation.Am J Transplant. 2020 Jan;20(1):172-180. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15560. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Am J Transplant. 2020. PMID: 31397943 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
First-In-Human, Phase 1, Randomized, Dose-Escalation Trial with Recombinant Anti-IL-20 Monoclonal Antibody in Patients with Psoriasis.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 7;10(8):e0134703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134703. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26252485 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and efficacy of HB0017, a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets interleukin-17A, in healthy participants and patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.Br J Dermatol. 2023 Dec 20;190(1):28-36. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad315. Br J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37669307 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of guselkumab in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a randomized, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study.Br J Dermatol. 2018 Mar;178(3):689-696. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16236. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Br J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29222947 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of alefacept, efalizumab, etanercept and infliximab in treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Br J Dermatol. 2008 Aug;159(2):274-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08673.x. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Br J Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18547300 Review.
Cited by
-
The Search for Biomarkers to Aid in Diagnosis, Differentiation, and Prognosis of Childhood Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome.Front Pediatr. 2019 Oct 16;7:404. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00404. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31681707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Costimulatory and Coinhibitory Immune Checkpoints in Atherosclerosis: Therapeutic Targets in Atherosclerosis?JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024 Mar 13;9(6):827-843. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.12.007. eCollection 2024 Jun. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39070270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the TNF and TNFR superfamilies in autoimmune disease and cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Dec;23(12):939-961. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01053-9. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39448880 Review.
-
Differential induction of donor-reactive Foxp3+ regulatory T cell via blockade of CD154 vs CD40.Am J Transplant. 2024 Aug;24(8):1369-1381. doi: 10.1016/j.ajt.2024.03.033. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Am J Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38552961 Free PMC article.
-
New molecular targets in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2024 May 1;36(3):235-240. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000001000. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38165286 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albach, F. N. , Wagner, F. , Hüser, A. , Igel, J. , Joseph, D. , Hilbert, J. , … Steffgen, J. (2018). Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single rising doses of BI 655064, an antagonistic anti‐CD40 antibody in healthy subjects: a potential novel treatment for autoimmune diseases. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 74, 161–169. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoyagi, T. , Yamashita, K. , Suzuki, T. , Uno, M. , Goto, R. , Taniguchi, M. , … Todo, S. (2009). A human anti‐CD40 monoclonal antibody, 4D11, for kidney transplantation in cynomolgus monkeys: induction and maintenance therapy. American Journal of Transplantation, 9, 1732–1741. - PubMed
-
- Bensinger, W. , Maziarz, R. T. , Jagannath, S. , Spencer, A. , Durrant, S. , Becker, P. S. , … Stadtmauer, E. A. (2012). A phase 1 study of lucatumumab, a fully human anti‐CD40 antagonist monoclonal antibody administered intravenously to patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. British Journal of Haematology, 159, 58–66. - PubMed
-
- van de Kerkhof, P. C. M. , Reich, K. , Kavanaugh, A. , Bachelez, H. , Barker, J. , Girolomoni, G. , … Lebwohl, M. G. (2015). Physician perspectives in the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: results from the population‐based Multinational Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis survey. Journal of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 29, 2002–2010. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

