Acute dose of melatonin via Nrf2 dependently prevents acute ethanol-induced neurotoxicity in the developing rodent brain
- PMID: 29679979
- PMCID: PMC5911370
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-018-1157-x
Acute dose of melatonin via Nrf2 dependently prevents acute ethanol-induced neurotoxicity in the developing rodent brain
Abstract
Background: Melatonin is a well-known potent endogenous antioxidant pharmacological agent with significant neuroprotective actions. Here in the current study, we explored the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) gene-dependent antioxidant mechanism underlying the neuroprotective effects of the acute melatonin against acute ethanol-induced elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the developing rodent brain.
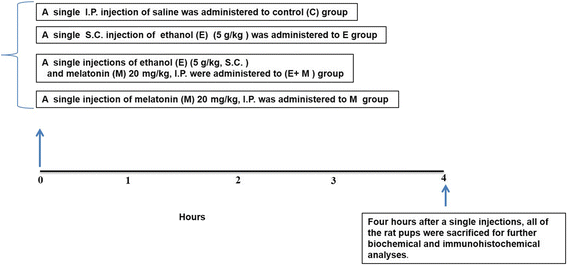
Methods: In vivo rat pups were co-treated with a single dose of acute ethanol (5 g/kg, subcutaneous (S.C.)) and a single dose of acute melatonin (20 mg/kg, intraperitoneal (I.P.)). Four hours after a single S.C. and I.P. injections, all of the rat pups were sacrificed for further biochemical (Western blotting, ROS- assay, LPO-assay, and immunohistochemical) analyses. In order to corroborate the in vivo results, we used the in vitro murine-hippocampal HT22 and microglial BV2 cells, which were subjected to knockdown with small interfering RNA (siRNA) of Nrf2 genes and exposed with melatonin (100 μM) and ethanol (100 mM) and proceed for further biochemical analyses.
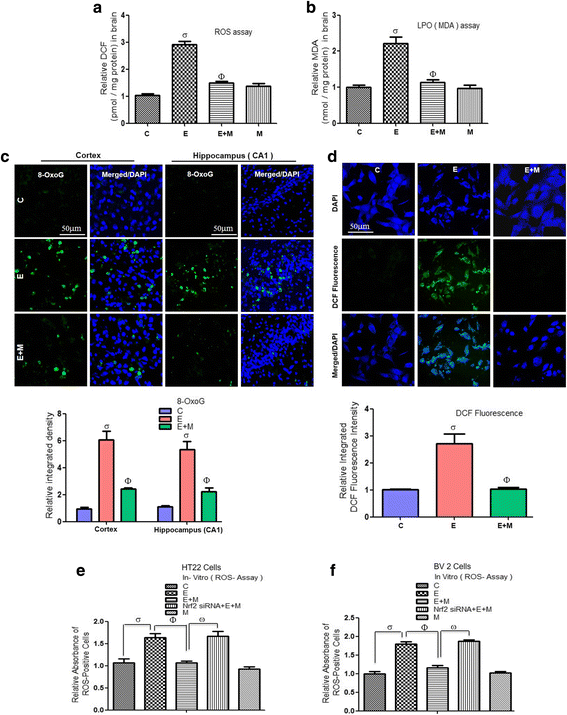
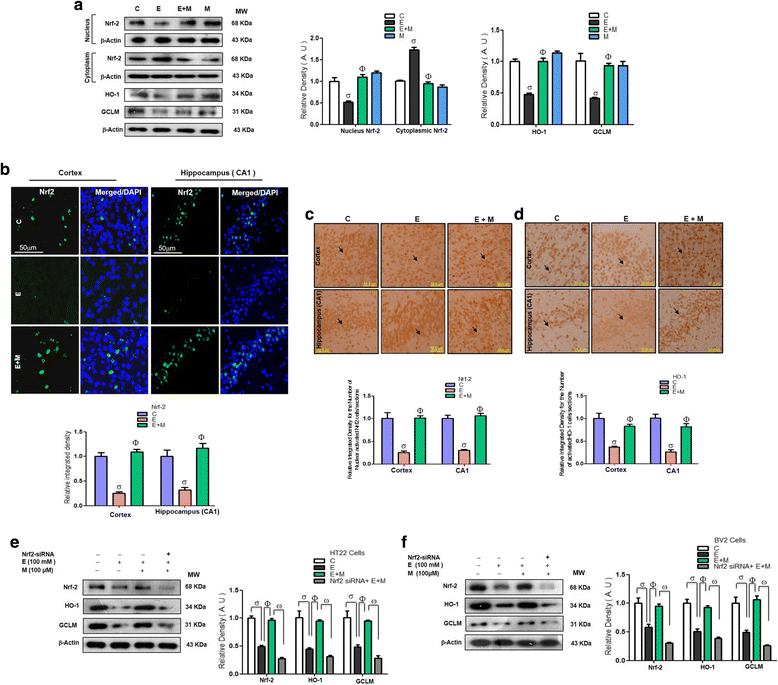
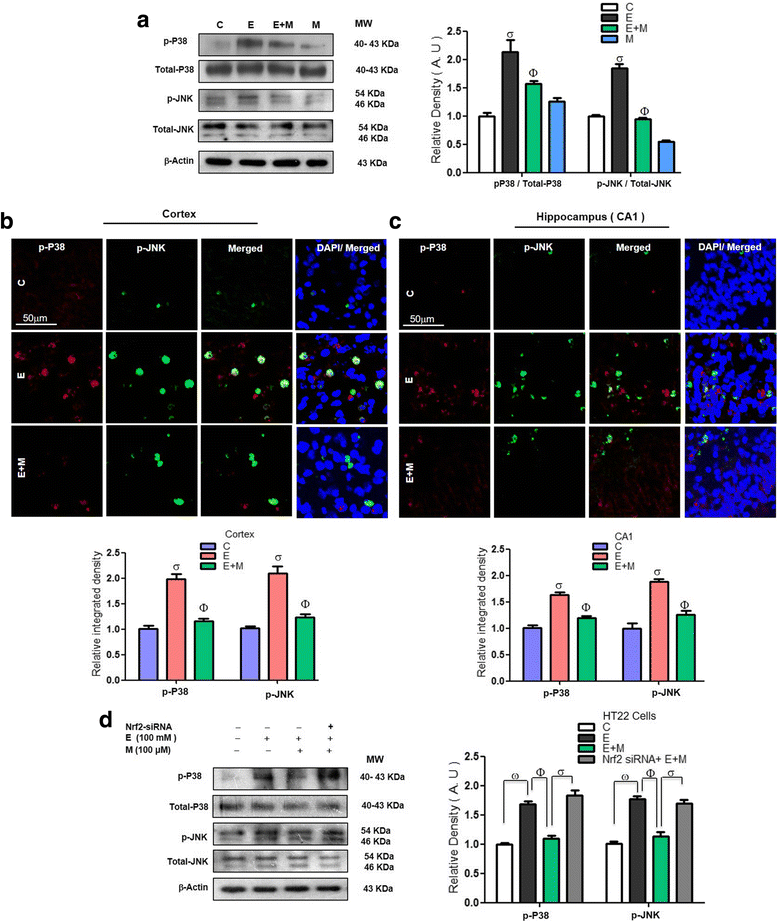
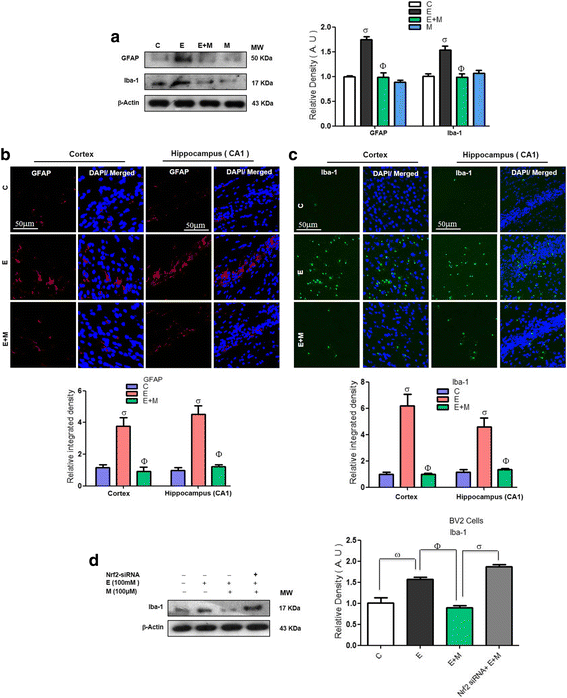
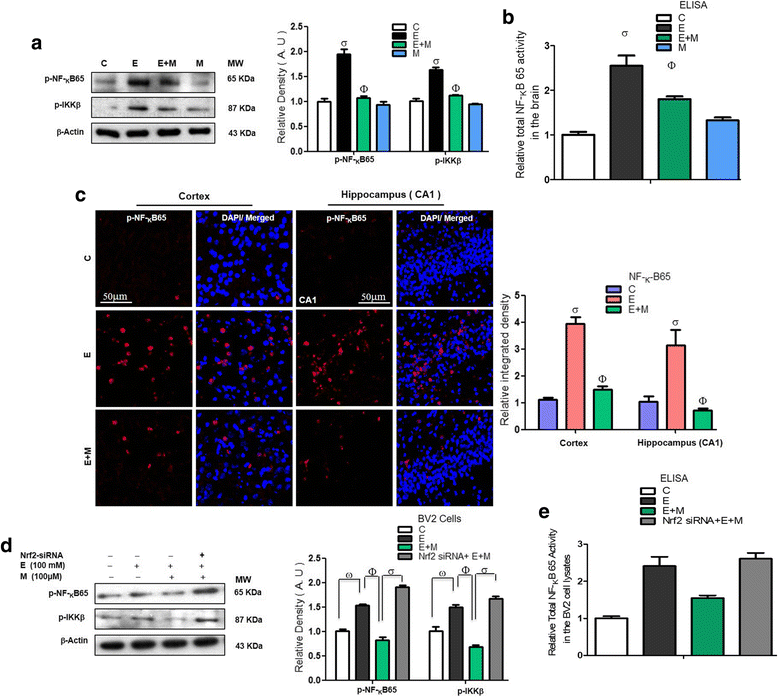
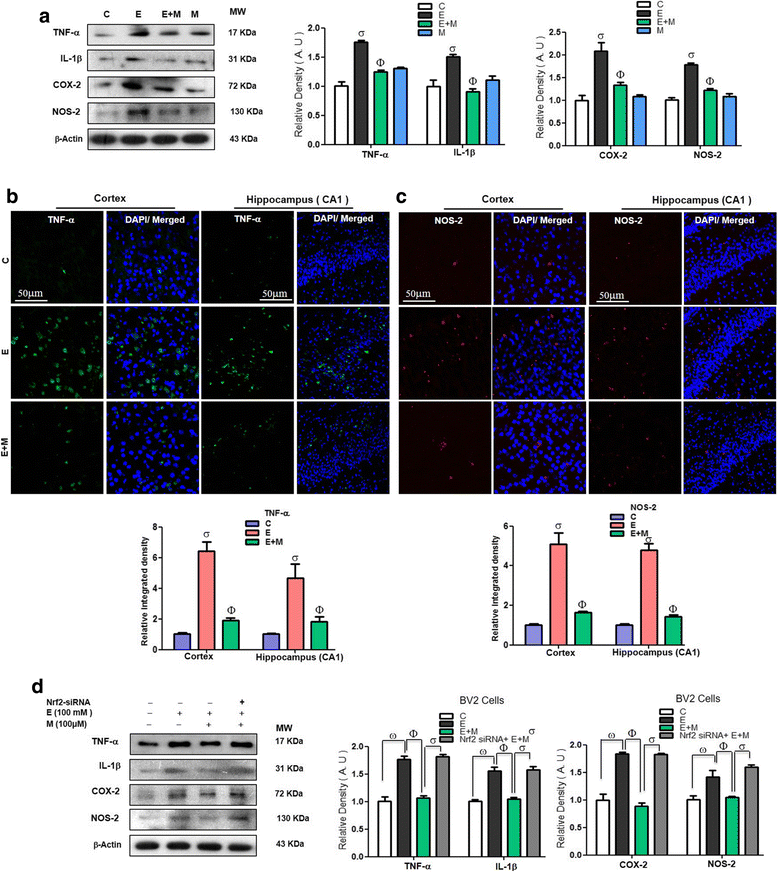
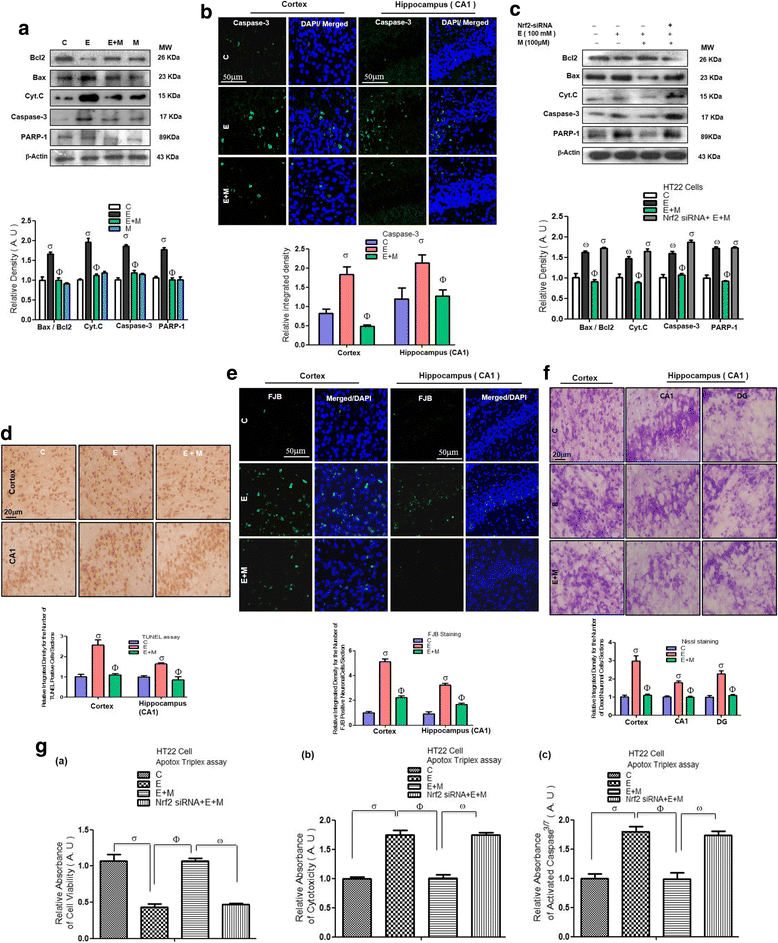
Results: Our biochemical, immunohistochemical, and immunofluorescence results demonstrate that acute melatonin significantly upregulated the master endogenous antioxidant Nrf2 and heme oxygenase-1, consequently reversing the acute ethanol-induced elevated ROS and oxidative stress in the developing rodent brain, and in the murine-hippocampal HT22 and microglial BV2 cells. In addition, acute melatonin subsequently reduced the activated MAPK-p-P38-JNK pathways and attenuated neuroinflammation by decreasing the expression of activated gliosis and downregulated the p-NF-K-B/p-IKKβ pathway and decreased the expression levels of other inflammatory markers in the developing rodent brain and BV2 cells. Of note, melatonin acted through the Nrf2-dependent mechanism to attenuate neuronal apoptosis in the postnatal rodent brain and HT22 cells. Immunohistofluorescence results also showed that melatonin prevented ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in the developing rodent brain. The in vitro results indicated that melatonin induced neuroprotection via Nrf2-dependent manner and reduced ethanol-induced neurotoxicity.
Conclusions: The pleiotropic and potent neuroprotective antioxidant characteristics of melatonin, together with our in vivo and in vitro findings, suppose that acute melatonin could be beneficial to prevent and combat the acute ethanol-induced neurotoxic effects, such as elevated ROS, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration in the developing rodent brain.
Keywords: Ethanol; MAPK-p-P38-JNK pathway; Melatonin; Neurodegeneration; Neuroinflammation; Neurotoxicity; Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2); ROS/oxidative stress; p-NF-K-B/p-IKKβ pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All the experiments with animal and other experimental protocols and procedures were approved (Approval ID: 125) by the Ethics Review Committee of the Gyeongsang National University, Republic of Korea.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

