Phase II Study of Paclitaxel and Dasatinib in Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29680193
- PMCID: PMC6682312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clbc.2018.03.010
Phase II Study of Paclitaxel and Dasatinib in Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Overexpression and activation of tyrosine kinase Src has been linked to breast carcinogenesis and bone metastases. We showed the feasibility of combining the SRC inhibitor dasatinib with weekly paclitaxel in patients with metastatic breast cancer (MBC) and herein report the subsequent phase II trial.
Patients and methods: Patients had received ≤ 2 chemotherapy regimens for measurable, HER2-negative MBC. Patients received paclitaxel and dasatinib (120 mg daily) and were assessed according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors for overall response rate (ORR), the primary end point. Secondary end points included progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). A 30% ORR (n = 55) was deemed worthy of further investigation. Exploratory biomarkers included N-telopeptide (NTX) and plasma vascular epidermal growth factor (VEGF) receptor 2 as predictors of clinical benefit.
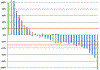
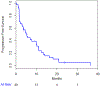
Results: From March 2010 to March 2014, 40 patients, including 2 men enrolled. The study was stopped early because of slow accrual. Overall, 32 patients (80%) had estrogen receptor-positive tumors and 23 (58%) had previously received taxanes. Of the 35 assessable patients, 1 (3%) had complete response and 7 (20%) partial response, resulting in an ORR of 23%. The median PFS and OS was 5.2 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.9-9.9) and 20.6 (95% CI, 12.9-25.2) months, respectively. As expected, fatigue (75%), neuropathy (65%), and diarrhea (50%) were common side effects, but were generally low-grade. Median baseline NTX was similar in patients who had clinical benefit (8.2 nmol BCE) and no clinical benefit (10.9 nmol BCE). Similarly, median baseline VEGF levels were similar between the 2 groups; 93.0 pg/mL versus 83.0 pg/mL.
Conclusion: This phase II study of dasatinib and paclitaxel was stopped early because of slow accrual but showed some clinical activity. Further study is not planned.
Keywords: Advanced breast cancer; Dasatinib; Metastatic breast cancer; Paclitaxel; SRC.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Dasatinib in breast cancer: Src-ing for response in all the wrong kinases.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Nov;6(Suppl 1):S60. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.10.26. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30613635 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mayer EL, Krop IE. Advances in targeting SRC in the treatment of breast cancer and other solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:3526–3532. - PubMed
-
- Finn RS. Targeting Src in breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:1379–1386. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek BS, Vroom TM, Adriaansen-Slot SS, et al. c-Src protein expression is increased in human breast cancer. An immunohistochemical and biochemical analysis. J Pathol. 1996;180:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Myoui A, Nishimura R, Williams PJ, et al. C-SRC tyrosine kinase activity is associated with tumor colonization in bone and lung in an animal model of human breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5028–5033. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki T, Sanjay A, Neff L, Tanaka S, Horne WC, Baron R. Src kinase activity is essential for osteoclast function. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:17660–17666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

