The Continuing Challenge of Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibition: Mechanism Matters
- PMID: 29680579
- PMCID: PMC6005755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.03.007
The Continuing Challenge of Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibition: Mechanism Matters
Abstract
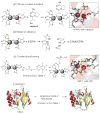
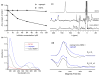
Metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) are a significant clinical problem because they hydrolyze and inactivate nearly all β-lactam-containing antibiotics. These 'lifesaving drugs' constitute >50% of the available contemporary antibiotic arsenal. Despite the global spread of MBLs, MBL inhibitors have not yet appeared in clinical trials. Most MBL inhibitors target active site zinc ions and vary in mechanism from ternary complex formation to metal ion stripping. Importantly, differences in mechanism can impact pharmacology in terms of reversibility, target selectivity, and structure-activity relationship interpretation. This review surveys the mechanisms of MBL inhibitors and describes methods that determine the mechanism of inhibition to guide development of future therapeutics.
Keywords: inhibitor; mechanism; metallo-β-lactamase; spectroscopy.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
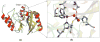

References
-
- Fisher JF, et al. Bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics: compelling opportunism, compelling opportunity. Chem Rev. 2005;105:395–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

