CapZyme-Seq Comprehensively Defines Promoter-Sequence Determinants for RNA 5' Capping with NAD<sup/>
- PMID: 29681497
- PMCID: PMC5935523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.03.014
CapZyme-Seq Comprehensively Defines Promoter-Sequence Determinants for RNA 5' Capping with NAD<sup/>
Abstract
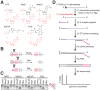
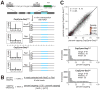
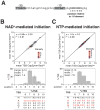
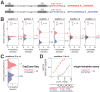
Nucleoside-containing metabolites such as NAD+ can be incorporated as 5' caps on RNA by serving as non-canonical initiating nucleotides (NCINs) for transcription initiation by RNA polymerase (RNAP). Here, we report CapZyme-seq, a high-throughput-sequencing method that employs NCIN-decapping enzymes NudC and Rai1 to detect and quantify NCIN-capped RNA. By combining CapZyme-seq with multiplexed transcriptomics, we determine efficiencies of NAD+ capping by Escherichia coli RNAP for ∼16,000 promoter sequences. The results define preferred transcription start site (TSS) positions for NAD+ capping and define a consensus promoter sequence for NAD+ capping: HRRASWW (TSS underlined). By applying CapZyme-seq to E. coli total cellular RNA, we establish that sequence determinants for NCIN capping in vivo match the NAD+-capping consensus defined in vitro, and we identify and quantify NCIN-capped small RNAs (sRNAs). Our findings define the promoter-sequence determinants for NCIN capping with NAD+ and provide a general method for analysis of NCIN capping in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: NudC; RNA capping; RNA polymerase; RNA-seq; Rai1; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; non-canonical initiating nucleotide; transcription; transcription initiation; transcription start site.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mechanism of RNA 5′ capping with NAD+, NADH and desphospho-CoA.Nature. 2016 Jul 21;535(7612):444-7. doi: 10.1038/nature18622. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27383794 Free PMC article.
-
CapZyme-Seq: A 5'-RNA-Seq Method for Differential Detection and Quantitation of NAD-Capped and Uncapped 5'-Triphosphate RNA.STAR Protoc. 2020 Jun 19;1(1):100002. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2019.100002. Epub 2020 Jun 3. STAR Protoc. 2020. PMID: 32719830 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Capping by Transcription Initiation with Non-canonical Initiating Nucleotides (NCINs): Determination of Relative Efficiencies of Transcription Initiation with NCINs and NTPs.Bio Protoc. 2017 Jun 20;7(12):e2336. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2336. Bio Protoc. 2017. PMID: 28840175 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical RNA-capping: Discovery, mechanism, and physiological role debate.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Mar;10(2):e1512. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1512. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30353673 Review.
-
RNA capping by mitochondrial and multi-subunit RNA polymerases.Transcription. 2018;9(5):292-297. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2018.1456258. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Transcription. 2018. PMID: 29624107 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ONE-seq: epitranscriptome and gene-specific profiling of NAD-capped RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 25;51(2):e12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1136. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36477375 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel NAD-RNA Decapping Pathway Discovered by Synthetic Light-Up NAD-RNAs.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 28;10(4):513. doi: 10.3390/biom10040513. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32231086 Free PMC article.
-
Use of NAD tagSeq II to identify growth phase-dependent alterations in E. coli RNA NAD+ capping.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 6;118(14):e2026183118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026183118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33782135 Free PMC article.
-
Np4A alarmones function in bacteria as precursors to RNA caps.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Feb 18;117(7):3560-3567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1914229117. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32019889 Free PMC article.
-
NAD tagSeq reveals that NAD+-capped RNAs are mostly produced from a large number of protein-coding genes in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jun 11;116(24):12072-12077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903683116. Epub 2019 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31142650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artsimovitch I, Svetlov V, Murakami KS, Landick R. Co-overexpression of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase subunits allows isolation and analysis of mutant enzymes lacking lineage-specific sequence insertions. JBC. 2003;278:12344–12355. - PubMed
-
- Barvik I, Rejman D, Panova N, Sanderova H, Krasny L. Non-canonical transcription initiation: the expanding universe of transcription initiating substrates. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017;41:131–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

