The effects of bevacizumab treatment in a rat model of retinal ischemia and perfusion injury
- PMID: 29681725
- PMCID: PMC5893009
The effects of bevacizumab treatment in a rat model of retinal ischemia and perfusion injury
Abstract
Purpose: To create a model of an ischemic retina with temporary ischemia and reperfusion (IR) and to examine the possible antiapoptotic and neurodegenerative effects of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antagonist.
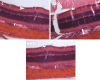
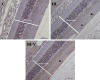
Methods: Three groups were formed. Rats were subjected to continued ischemia for 45 min, and then reperfusion was allowed for 2 days. For the first group, ischemia was induced, but an anti-VEGF agent was not administered. For the second group, 2 days before ischemia, 0.005 ml (0.125 mg) of bevacizumab was administered intravitreally, and then the ischemic model was created. The last group's intraocular pressure was not increased as in the control group, and only a cannula was introduced into the anterior chamber through the cornea. Six animals from each group were subjected to histomorphometry, and four were subjected to immunohistochemical and histopathologic examinations. For a histomorphometric examination, the number of cells in the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer was counted using the optical dissector method. For immunohistochemistry, the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) levels and apoptosis were examined in the retinal and choroidal tissue.
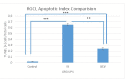
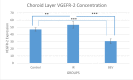
Results: It was observed that in an IR injury, bevacizumab reduces the death and apoptosis of cells in the RGC layer. It was also identified that although bevacizumab is a large molecule, the agent affects the choroid and reduces the amount of VEGFR-2 in this tissue.
Conclusions: IR may be used as a model of ischemic retinopathy that includes VEGF-dependent vascular permeability and neurodegeneration. Although VEGF is a neurotrophic molecule, in IR injury, treatment with bevacizumab, which is an anti-VEGF agent, decreases apoptosis, showing that excess function of this molecule can be hazardous.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of ischemic preconditioning and bevacizumab on apoptosis and vascular permeability following retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Nov;51(11):5920-33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5264. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20554620
-
Effect of Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Antibody on the Survival of Cultured Retinal Ganglion Cells.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2017 Aug;31(4):360-365. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2017.0054. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28752700 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects on the retina after ranibizumab treatment in an ischemia model.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 11;12(8):e0182407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182407. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28800629 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-adhesive effect of anti-VEGF agents in experimental models: A systematic review.Wound Repair Regen. 2021 Jan;29(1):168-182. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12879. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Wound Repair Regen. 2021. PMID: 33316850
-
A Critical Review of Biological Properties, Delivery Systems and Analytical/Bioanalytical Methods for Determination of Bevacizumab.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2021;51(5):445-453. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2020.1743641. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 32295395 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Imaging of Ischemia/Reperfusion-mediated Aminopeptidase N Expression in Surgical Rat Model Using 68Ga-NOTA-c(NGR).In Vivo. 2022 Mar-Apr;36(2):657-666. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12750. In Vivo. 2022. PMID: 35241519 Free PMC article.
-
Bevacizumab or fibronectin gene editing inhibits the osteoclastogenic effects of fibroblasts derived from human radicular cysts.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Jul;40(7):949-956. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0172-x. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30382180 Free PMC article.
-
HIF inhibitor topotecan has a neuroprotective effect in a murine retinal ischemia-reperfusion model.PeerJ. 2019 Oct 4;7:e7849. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7849. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31592359 Free PMC article.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Parathyroid Organoids Resemble Parathyroid Morphology and Function.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Nov;11(43):e2407567. doi: 10.1002/advs.202407567. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39331961 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological role of vitamin D deficiency in recurrent/chronic tonsillitis pathogenesis: Vascular epithelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis in tonsil.Clin Exp Dent Res. 2022 Jun;8(3):699-706. doi: 10.1002/cre2.539. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2022. PMID: 35213796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen QD, Tatlipinar S, Shah SM, Haller JA, Quinlan E, Sung J, Zimmer-Galler I, Do DV, Campochiaro PA. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a critical stimulus for diabetic macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;142:961–9. - PubMed
-
- Zeng HY, Green WR, Tso MO. Microglial activation in human diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126:227–32. - PubMed
-
- Adamis AP, Berman AJ. Immunological mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Semin Immunopathol. 2008;30:65–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

