Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 29681949
- PMCID: PMC5850899
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/5416923
Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
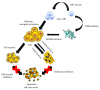
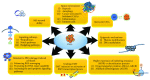
Cancer stem cells (CSCs), also known as tumor-initiating cells (TICs), are suggested to be responsible for drug resistance and cancer relapse due in part to their ability to self-renew themselves and differentiate into heterogeneous lineages of cancer cells. Thus, it is important to understand the characteristics and mechanisms by which CSCs display resistance to therapeutic agents. In this review, we highlight the key features and mechanisms that regulate CSC function in drug resistance as well as recent breakthroughs of therapeutic approaches for targeting CSCs. This promises new insights of CSCs in drug resistance and provides better therapeutic rationales to accompany novel anticancer therapeutics.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

