Standardization of the Manufacturing Process of Bee Venom Pharmacopuncture Containing Melittin as the Active Ingredient
- PMID: 29681969
- PMCID: PMC5845530
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/2353280
Standardization of the Manufacturing Process of Bee Venom Pharmacopuncture Containing Melittin as the Active Ingredient
Abstract
Background: Pharmacopuncture is a unique treatment in oriental medicine that combines chemical stimulation with conventional acupuncture. However, there are no standardized methods for preparing the herbal medicines used in pharmacopuncture, and it is not clear whether the active ingredients are safe and stable. Several studies have investigated nonstandardized preparation processes, but few investigations have addressed safety and preparation methods. Pharmacopuncture may provide an alternative treatment for incurable diseases. However, it must be as valid and safe as standardized medicine. In this way, the present project may contribute to the industrialization of medicine in Korea. It may also expand health insurance coverage by promoting evidence-based medical insurance benefits. Thus, the present study attempted to standardize and improve the raw materials, preparation, and efficacy of bee venom pharmacopuncture (BVP), which is a highly effective technique in oriental medicine.
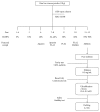
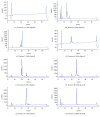
Method: To purify the crude bee venom, the extract was subjected to a stepped-gradient open column (ODS-A; 120 Å, 150 mesh). Using this method, the yield of melittin was significantly increased and the allergen proteins were effectively removed. The melittin content of the purified bee venom was determined using HPLC, and the product was then diluted to 0.1 mg/mL using injection water in preparation for BVP.
Results: In the present study, we standardized the purification process to provide safe and stable BVP by increasing the main effective components and eliminating allergens. This study will be seminal in the industrialization and regulation of BVP.
Conclusion: We developed an effective strategy for melittin purification and allergen removal from bee venom to create safe BVP.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigation of the Adverse Events Associated with Bee Venom Pharmacopuncture in Patients Hospitalized in a Korean Hospital: A Retrospective Chart Review Study.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;14(10):662. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100662. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287931 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Venom for Medical Usage in Pharmacopuncture in Korean Medicine: Current Status and Clinical Implication.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 1;13(2):105. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020105. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33535603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative study on the effects of bee venom pharmacopuncture according to the treatment method for knee osteoarthritis.J Pharmacopuncture. 2012 Dec;15(4):7-14. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2012.15.011. J Pharmacopuncture. 2012. PMID: 25780649 Free PMC article.
-
Research on Korean Pharmacopuncture in South Korea since 2007.J Pharmacopuncture. 2014 Dec;17(4):15-21. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2014.17.032. J Pharmacopuncture. 2014. PMID: 25780715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bee venom pharmacopuncture responses according to sasang constitution and gender.J Pharmacopuncture. 2013 Dec;16(4):43-8. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2013.16.023. J Pharmacopuncture. 2013. PMID: 25780682 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential and Mechanisms of Bee Venom Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Apitoxin Applications and Safety Enhancement Strategies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;17(9):1211. doi: 10.3390/ph17091211. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Processing Technologies for Bee Products: An Overview of Recent Developments and Perspectives.Front Nutr. 2021 Nov 3;8:727181. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.727181. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34805239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterologous expressing melittin in a probiotic yeast to evaluate its function for promoting NSC-34 regeneration.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 28;108(1):496. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13336-7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39466458 Free PMC article.
-
Melittin-Based Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Aug 6;17(8):1019. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17081019. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40871040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bee Venom Triggers Autophagy-Induced Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cells via the mTOR Signaling Pathway.J Oncol. 2022 Dec 23;2022:8916464. doi: 10.1155/2022/8916464. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36590307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute. Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute Compilation: A Pharmacopuncture Prepared from Herbs And Clinical Application. Seoul, Korea: Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute;
-
- Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute. Pharmacopuncturology. Seoul, Korea: Elsevier LLC; 2012. Chapter 1, Definition and history.
-
- Kim M.-R., Shin J.-S., Lee J., et al. Safety of acupuncture and pharmacopuncture in 80,523 musculoskeletal disorder patients: A retrospective review of internal safety inspection and electronic medical records. Medicine (United States) 2016;95(18):p. e3635. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003635. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ko H. K. Experimental Studies on the Effect of Bee Venom Theraphy on the Analgesic, Antipyretic and Anti-inflammatory Action. Korean journal of oriental medicine. 1992;no. 1:283–292.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

