A pilot hole does not reduce the strains or risk of fracture to the lateral cortex during and following a medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy in cadaveric specimens
- PMID: 29682282
- PMCID: PMC5895948
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.72.BJR-2017-0337.R1
A pilot hole does not reduce the strains or risk of fracture to the lateral cortex during and following a medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy in cadaveric specimens
Abstract
Aim: It has been suggested that the use of a pilot-hole may reduce the risk of fracture to the lateral cortex. Therefore the purpose of this study was to determine the effect of a pilot hole on the strains and occurrence of fractures at the lateral cortex during the opening of a high tibial osteotomy (HTO) and post-surgery loading.
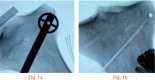
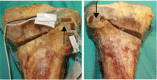
Materials and methods: A total of 14 cadaveric tibias were randomized to either a pilot hole (n = 7) or a no-hole (n = 7) condition. Lateral cortex strains were measured while the osteotomy was opened 9 mm and secured in place with a locking plate. The tibias were then subjected to an initial 800 N load that increased by 200 N every 5000 cycles, until failure or a maximum load of 2500 N.
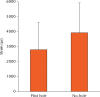
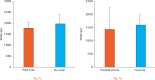
Results: There was no significant difference in the strains on the lateral cortex during HTO opening between the pilot hole and no-hole conditions. Similarly, the lateral cortex and fixation plate strains were not significantly different during cyclic loading between the two conditions. Using a pilot hole did not significantly decrease the strains experienced at the lateral cortex, nor did it reduce the risk of fracture.
Conclusions: The nonsignificant differences found here most likely occurred because the pilot hole merely translated the stress concentration laterally to a parallel point on the surface of the hole.Cite this article: K. Bujnowski, A. Getgood, K. Leitch, J. Farr, C. Dunning, T. A. Burkhart. A pilot hole does not reduce the strains or risk of fracture to the lateral cortex during and following a medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy in cadaveric specimens. Bone Joint Res 2018;7:166-172. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.72.BJR-2017-0337.R1.
Keywords: Fixation Plate; Fracture; High Tibial Osteotomy; Lateral Cortical Strains; Lateral cortex; Tibial osteotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement: SBM provided in-kind support for this project
Figures



References
-
- Bombardier C, Hawker G, Mosher D. The Impact of Arthritis in Canada: Today and over the next 30 years. Artritis Alliance of Canada, 2011.
-
- Khan M, Osman K, Green G, Haddad FS. The epidemiology of failure in total knee arthroplasty: avoiding your next revision. Bone Joint J 2016;98-B(suppl A):105-112. - PubMed
-
- Von Keudell A, Sodha S, Collins J, et al. Patient satisfaction after primary total and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: an age-dependent analysis. Knee 2014;21:180-184. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

