Overview on Clinical Relevance of Intra-Tumor Heterogeneity
- PMID: 29682505
- PMCID: PMC5897590
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00085
Overview on Clinical Relevance of Intra-Tumor Heterogeneity
Abstract
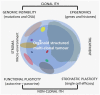
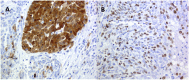
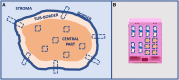
Today, clinical evaluation of tumor heterogeneity is an emergent issue to improve clinical oncology. In particular, intra-tumor heterogeneity (ITH) is closely related to cancer progression, resistance to therapy, and recurrences. It is interconnected with complex molecular mechanisms including spatial and temporal phenomena, which are often peculiar for every single patient. This review tries to describe all the types of ITH including morphohistological ITH, and at the molecular level clonal ITH derived from genomic instability and nonclonal ITH derived from microenvironment interaction. It is important to consider the different types of ITH as a whole for any patient to investigate on cancer progression, prognosis, and treatment opportunities. From a practical point of view, analytical methods that are widely accessible today, or will be in the near future, are evaluated to investigate the complex pattern of ITH in a reproducible way for a clinical application.
Keywords: cancer spreading; clonal intra-tumor heterogeneity; functional phenotypic plasticity; genomic instability; intra-tumor heterogeneity; morphohistological intra-tumor heterogeneity; stochastic plasticity.
Figures

References
-
- Davis C, Naci H, Gurpinar E, Poplavska E, Pinto A, Aggarwal A. Availability of evidence of benefits on overall survival and quality of life of cancer drugs approved by European Medicines Agency: retrospective cohort study of drug approvals 2009-13. BMJ (2017) 359:j4530.10.1136/bmj.j4530 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

