Tissue-based quantitative proteomics to screen and identify the potential biomarkers for early recurrence/metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 29683265
- PMCID: PMC6010861
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1463
Tissue-based quantitative proteomics to screen and identify the potential biomarkers for early recurrence/metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
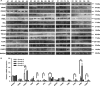
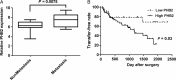
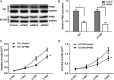
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the eighth cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. To screen potential biomarkers associated with early recurrence/metastasis (R/M) of ESCC patients after radical resection, ESCC patients were analyzed by a comparative proteomics analysis using iTRAQ with RPLC-MS to screen differential proteins among R/M groups and adjacent normal tissues. The proteins were identified by qRT-PCR, Western blotting, and tissue microarray. The protein and mRNA expression difference of PHB2 between tumor tissues of ESCC patients and adjacent normal tissues, ESCC patients with and without metastasis, four ESCC cell lines and normal esophageal epithelial cells were inspected using immunohistochemical staining, qRT-PCR, and Western blotting. The EC109 and TE1 cells were used to establish PHB2 knockdown cell models, and their cell proliferation and invasion ability were determined by cell counting method, Transwell® assay. Thirteen proteins were selected by cutoff value of 0.67 fold for underexpression and 1.5-fold for overexpression. Seven proteins were confirmed to be associated with R/M among the 13 proteins. The potential biomarker PHB2 for early recurrence/metastasis of ESCC was identified. PHB2 expression was related to the OS of ESCC patients (P = 0.032) and had high levels in the tumor tissues and human cell lines of ESCC (P = 0.0002). Also, the high PHB2 expression promoted the metastasis of ESCC (P = 0.0075), suggesting high PHB2 expression was a potential prognostic biomarker. Experiments showed that PHB2 could significantly promote the proliferation and cell invasion ability of human ESCC cell lines and the knockdown of PHB2 suppressed the phosphorylation level of AKT, as well as the expression of MMP9 and RAC1. PHB2 could predict the early metastasis of ESCC patients.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; metastasis; proteomic; recurrence; tissue microarray.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Effects of microRNA-182-5p on cell proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and related molecular mechanisms].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020 Aug 23;42(8):635-643. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200310-00191. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32867454 Chinese.
-
Long non-coding RNA DUXAP8 regulates proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell cancer.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(9):2646-2652. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_14959. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29771416
-
[Expression of microRNA-17-5p in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its effects on cell proliferation and invasion].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 23;42(2):105-113. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2020.02.004. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32135643 Chinese.
-
CD82/KAI1 inhibits invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via TGF-β1.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Sep;22(18):5928-5937. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201809_15922. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30280774
-
[MicroRNA-133b suppresses cell proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via downregulating TAGLN2 expression].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019 Feb 23;41(2):91-96. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.02.003. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30862136 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Mitophagy in Cancer: A Tale of Adaptation.Cells. 2019 May 22;8(5):493. doi: 10.3390/cells8050493. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31121959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Characterization of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using Quantitative Proteomics.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 23;15(13):3302. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133302. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444412 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating plasma proteomes with genome-wide association data for causal protein identification in multiple myeloma.BMC Med. 2023 Sep 29;21(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03086-0. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37775746 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Protein PHB2 and Its Regulatory Mechanisms in Cancer.Cells. 2023 Apr 21;12(8):1211. doi: 10.3390/cells12081211. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Target Score-A Proteomics Data Selection Tool Applied to Esophageal Cancer Identifies GLUT1-Sialyl Tn Glycoforms as Biomarkers of Cancer Aggressiveness.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 7;22(4):1664. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041664. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33562270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel, R. L. , Miller K. D., and Jemal A.. 2016. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Chen, W. , Zheng R., Baade P. D., Zhang S., Zeng H., Bray F., et al. 2015. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Rustgi, A. K. , and El‐Serag H. B.. 2014. Esophageal carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 371:2499–2509. - PubMed
-
- Mariette, C. , Piessen G., and Triboulet J. P.. 2007. Therapeutic strategies in oesophageal carcinoma: role of surgery and other modalities. Lancet Oncol. 8:545–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

