CaC3H14 encoding a tandem CCCH zinc finger protein is directly targeted by CaWRKY40 and positively regulates the response of pepper to inoculation by Ralstonia solanacearum
- PMID: 29683552
- PMCID: PMC6638151
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12694
CaC3H14 encoding a tandem CCCH zinc finger protein is directly targeted by CaWRKY40 and positively regulates the response of pepper to inoculation by Ralstonia solanacearum
Abstract
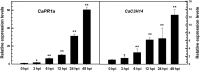
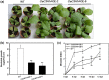
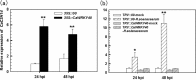
Tandem CCCH zinc finger (TZnF) proteins have been implicated in plant defence, but their role in pepper (Capsicum annuum) is unclear. In the present study, the role of CaC3H14, a pepper TZnF protein, in the immune response of pepper plants to Ralstonia solanacearum infection was characterized. When fused to the green fluorescent protein, CaC3H14 was localized exclusively to the nuclei in leaf cells of Nicotiana benthamiana plants transiently overexpressing CaC3H14. Transcript abundance of CaC3H14 was up-regulated by inoculation with R. solanacearum. Virus-induced silencing of CaC3H14 increased the susceptibility of the plants to R. solanacearum and down-regulated the genes associated with the hypersensitive response (HR), specifically HIR1 and salicylic acid (SA)-dependent PR1a. By contrast, silencing resulted in the up-regulation of jasmonic acid (JA)-dependent DEF1 and ethylene (ET) biosynthesis-associated ACO1. Transient overexpression of CaC3H14 in pepper triggered an intensive HR, indicated by cell death and hydrogen peroxide (H2 O2 ) accumulation, up-regulated PR1a and down-regulated DEF1 and ACO1. Ectopic overexpression of CaC3H14 in tobacco plants significantly decreased the susceptibility of tobacco plants to R. solanacearum. It also up-regulated HR-associated HSR515, immunity-associated GST1 and the SA-dependent marker genes NPR1 and PR2, but down-regulated JA-dependent PR1b and ET-dependent EFE26. The CaC3H14 promoter and was bound and its transcription was up-regulated by CaWRKY40. Collectively, these results indicate that CaC3H14 is transcriptionally targeted by CaWRKY40, is a modulator of the antagonistic interaction between SA and JA/ET signalling, and enhances the defence response of pepper plants to infection by R. solanacearum.
Keywords: Capsicum annuum; Ralstonia solanacearum; CCCH-type zinc finger; immunity.
© 2018 BSPP and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Addepalli, B. and Hunt, A.G. (2008) Ribonuclease activity is a common property of Arabidopsis CCCH‐containing zinc‐finger proteins. FEBS Lett. 582, 2577–2582. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal, P. , Reddy, M.P. and Chikara, J. (2011) WRKY: its structure, evolutionary relationship, DNA‐binding selectivity, role in stress tolerance and development of plants. Mol. Biol. Rep. 38, 3883–3896. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch, M. , Gobbato, E. , Bednarek, P. , Debey, S. , Schultze, J.L. , Bautor, J. and Parker, J.E. (2006) Salicylic acid‐independent ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 signaling in Arabidopsis immunity and cell death is regulated by the monooxygenase FMO1 and the Nudix hydrolase NUDT7. Plant Cell, 18, 1038–1051. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

