Serum galactomannan antigen as a prognostic and diagnostic marker for invasive aspergillosis in heterogeneous medicine ICU patient population
- PMID: 29684057
- PMCID: PMC5912734
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196196
Serum galactomannan antigen as a prognostic and diagnostic marker for invasive aspergillosis in heterogeneous medicine ICU patient population
Abstract
Objective: This study was conducted to get a complete clinical and mycological picture of invasive aspergillosis (IA) in respiratory medicine ICU of a tertiary care hospital.
Patients: From the cohort of 235 patients only one had proven IA. Based on AspICU algorithm, 21 had putative IA (8.9%), 12 were colonised (5.1%).
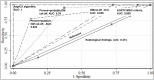
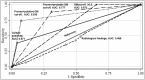
Results: Adjusting the confounding factors, significant risk factors for IA were chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), temperature of ≥38°C, pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The best predictor of IA was AspICU algorithm (AUC, 1) followed by serum galactomannan antigen (GM) cut-off (≥1.24) calculated based on AspICU algorithm (AUC, 0.822). For 37% of patients, IA diagnoses was made earlier with serum GM than radiology. There were 70/235 (29.8%) deaths within 30 days of enrolment in the study. Aspergillus culture positivity (34/235, 14.5%) was associated with very high mortality (27/34, 79.4%), (p<0.05). The best predictor of mortality was GM cut-off (≥1.24) calculated based on AspICU algorithm (AUC, 0.835).
Conclusion: This study imparts the focus on relatively underestimated Aspergillus infections prevalent in ICUs. The AspICU algorithm was found to be useful over others for IA diagnosis. The prognostic usefulness of serum GM antigen detection test highlighted overlooking the same may not be rewarding for the outcome of IA suspected ICU subpopulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of serum galactomannan in mixed ICU patients: a retrospective observational study.Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2014 Jul-Aug;46(3):145-54. doi: 10.5603/AIT.2014.0027. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2014. PMID: 25078766
-
Galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: a tool for diagnosing aspergillosis in intensive care unit patients.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Jan 1;177(1):27-34. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200704-606OC. Epub 2007 Sep 20. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 17885264
-
Serum galactomannan versus a combination of galactomannan and polymerase chain reaction-based Aspergillus DNA detection for early therapy of invasive aspergillosis in high-risk hematological patients: a randomized controlled trial.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Feb 1;60(3):405-14. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu833. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25336623 Clinical Trial.
-
Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Review of definitions and diagnostic approaches.Mycoses. 2021 Sep;64(9):1002-1014. doi: 10.1111/myc.13274. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Mycoses. 2021. PMID: 33760284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Usefulness of galactomannan detection in the diagnosis and follow-up of hematological patients with invasive aspergillosis].Rev Iberoam Micol. 2003 Sep;20(3):103-10. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2003. PMID: 15456366 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of Serum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Galactomannan Levels in Invasive Aspergillosis: An 8-Year Experience at a Tertiary Cancer Center.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 May 3;11(5):355. doi: 10.3390/jof11050355. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422689 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Diagnostic Criteria for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Critically Ill Patients.Infect Dis Ther. 2023 Jun;12(6):1641-1653. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00818-w. Epub 2023 May 18. Infect Dis Ther. 2023. PMID: 37199881 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of pleural aspergillosis: a review of 13 cases.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Apr 2;12(4):e0385223. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03852-23. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38411055 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Serum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Galactomannan in Diagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2019 Feb 27;57(3):e01821-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01821-18. Print 2019 Mar. J Clin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30626661 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors and outcomes of peritoneal dialysis-related infections due to filamentous molds (MycoPDICS).PLoS One. 2022 May 24;17(5):e0268823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268823. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35609049 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

