Comparative analysis of tissue reconstruction algorithms for 3D histology
- PMID: 29684099
- PMCID: PMC6129300
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty210
Comparative analysis of tissue reconstruction algorithms for 3D histology
Abstract
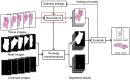
Motivation: Digital pathology enables new approaches that expand beyond storage, visualization or analysis of histological samples in digital format. One novel opportunity is 3D histology, where a three-dimensional reconstruction of the sample is formed computationally based on serial tissue sections. This allows examining tissue architecture in 3D, for example, for diagnostic purposes. Importantly, 3D histology enables joint mapping of cellular morphology with spatially resolved omics data in the true 3D context of the tissue at microscopic resolution. Several algorithms have been proposed for the reconstruction task, but a quantitative comparison of their accuracy is lacking.
Results: We developed a benchmarking framework to evaluate the accuracy of several free and commercial 3D reconstruction methods using two whole slide image datasets. The results provide a solid basis for further development and application of 3D histology algorithms and indicate that methods capable of compensating for local tissue deformation are superior to simpler approaches.
Availability and implementation: Code: https://github.com/BioimageInformaticsTampere/RegBenchmark. Whole slide image datasets: http://urn.fi/urn: nbn: fi: csc-kata20170705131652639702.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures


References
-
- Amunts K. et al. (2013) BigBrain: an ultrahigh-resolution 3D human brain model. Science, 340, 1472–1475. - PubMed
-
- Arganda-Carreras I. et al. (2006) Consistent and elastic registration of histological sections using vector-spline regularization. In: International Workshop on Computer Vision Approaches to Medical Image Analysis, pp. 85–95.
-
- Arganda‐Carreras I. et al. (2010) 3D reconstruction of histological sections: application to mammary gland tissue. Microsci. Res. Technol., 73, 1019–1029. - PubMed
-
- Beare R. et al. (2008) An assessment of methods for aligning two-dimensional microscope sections to create image volumes. J. Neurosci. Methods, 170, 332–344. - PubMed
-
- Braumann U. et al. (2005) Three-dimensional reconstruction and quantification of cervical carcinoma invasion fronts from histological serial sections. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 24, 1286–1307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

