Moving towards an organized cervical cancer screening: costs and impact
- PMID: 29684144
- PMCID: PMC6241209
- DOI: 10.1093/eurpub/cky061
Moving towards an organized cervical cancer screening: costs and impact
Abstract
Background: HPV screening has been shown to be more cost-effective than cytology screening under most scenarios. Furthermore, it should be offered only in organized programmes with good quality assurance mechanisms. This study analyses the comparative cost of the current policy of opportunistic cytology screening vs. a hypothetical organized programme based on primary HPV screening.
Methods: Total cervical cancer expenditure was defined as the sum of three cost elements: (i) direct (medical and non-medical) costs, obtained from a calibrated Markov model of the natural history of HPV and cervical cancer; (ii) programmatic costs, estimated based on other organized screening programmes; and (iii) indirect costs, extrapolated from previously published data.
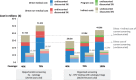
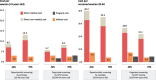
Results: Organized HPV screening at 5-year intervals costs consistently less across all coverage levels than opportunistic cytology screening at 3-year intervals. The current annual direct medical cost to the public health system of the opportunistic cytology at 40% coverage is estimated at €33.2 per woman screened aged 25-64. Under an organized programme of primary HPV screening at 70% coverage, the cost is estimated to be €18.4 per woman screened aged 25-64.
Conclusion: Our study concludes that the economic resources currently devoted to providing opportunistic cytology screening to 40% of the target population at 3-year intervals could be more effectively used to screen 70% of the target population at 5-year intervals by switching to an organized programme based on primary HPV screening. This finding is of relevance to other European countries or regions with similar screening policies and health infrastructures.
Figures
References
-
- Sullivan SD, Mauskopf JA, Augustovski F, et al.Budget impact analysis-principles of good practice: report of the ISPOR 2012 budget impact analysis good practice II task force. Value Health 2014; 17:5–14. - PubMed
-
- Guidelines for the Economic Evaluation of Health Technologies: Canada [Internet]. Methods and Guidelines | CADTH.ca. 4th edn, 2018. Available at: https://www.cadth.ca/about-cadth/how-we-do-it/methods-and-guidelines (12 March 2018, date last accessed).
-
- Zaza S, Briss PA, Harris KW, editors. The Guide to Community Preventive Services: What Works to Promote Health? [Internet]. Task Force on Community Preventive Services. Atlanta: Oxford University Press, 2005. Available at: http://www.oxfordscholarship.com/view/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195151091.0... (4 August 2015, date last accessed). - DOI
-
- Nieminen P, Kallio M, Anttila A, Hakama M. Organised vs. spontaneous Pap-smear screening for cervical cancer: a case-control study. Int J Cancer 1999; 83:55–8. - PubMed
-
- Virtanen A, Anttila A, Luostarinen T, Malila N, Nieminen P. Improving cervical cancer screening attendance in Finland. Int J Cancer 2014; 136:E677–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

