Wirsung atraumatic rupture in patient with pancreatic pseudocysts: a case presentation
- PMID: 29685110
- PMCID: PMC5913810
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0781-3
Wirsung atraumatic rupture in patient with pancreatic pseudocysts: a case presentation
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic duct disruption is a challenging condition leading to pancreatic juice leakage and consequently to pancreatic fluid collections. The manifestations of pancreatic main duct leak include pseudocysts, walled-off necrosis, pancreatic fistulas, ascites, pleural and pericardial effusions. Pseudocyst formation is the most frequent outcome of a pancreatic duct leak.
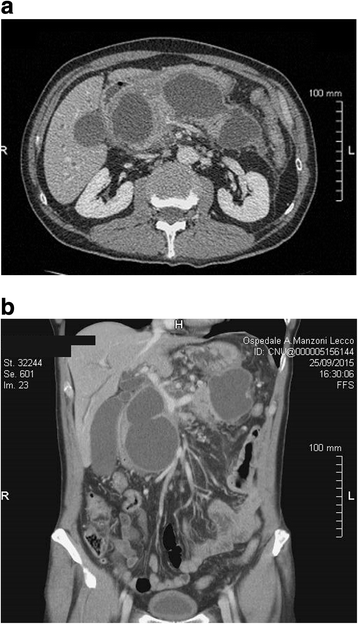
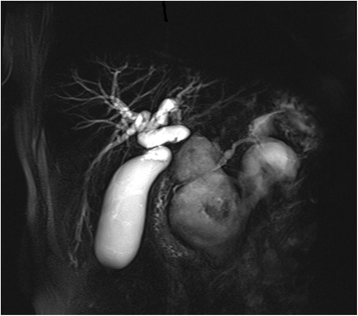
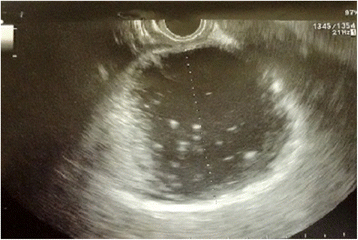
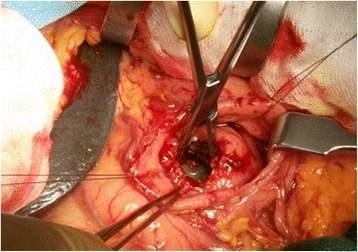
Case presentation: We describe a case of a 64-year old man with large multiple pancreatic cysts discovered for progressive jaundice and significant weight loss in the absence of a previous episode of acute pancreatitis. Computed tomography scan showed lesion with thick enhancing walls. The main cyst dislocated the stomach and the duodenum inducing intra and extrahepatic bile ducts enlargement. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed a communication between the main pancreatic duct and the cystic lesions due to Wirsung duct rupture. Endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration cytology did not show neoplastic cells and cyst fluid analysis revealed high amylase concentration. Preoperative exams were suggestive but not conclusive for a benign lesion. Laparotomy was necessary to confirm the presence of large communicating pseudocysts whose drainage was performed by cystogastrostomy. Histology confirmed the inflammatory nature of the cyst wall. Subsequently, the patient had progressive jaundice resolution.
Conclusion: Pancreatic cystic masses include several pathological entities, ranging from benign to malignant lesions. Rarely pseudocysts present as complex cystic pancreatic lesions with biliary compression in absence of history of acute pancreatitis. We describe the rare case of multiple pancreatic pseudocysts due to Wirsung duct rupture in absence of previous trauma or acute pancreatitis. Magnetic resonance showed the presence of communication with the main pancreatic duct and endoscopic ultrasound fine needle aspiration suggested the benign nature of the lesion.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Jaundice; Pancreatic cystic mass; Pancreatic duct rupture; Pseudocyst.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this Case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available on request.
Competing interests
None of the contributing authors have any conflict of interest, including specific financial interests or relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EUS-assisted rendezvous stenting of the pancreatic duct for chronic calcifying pancreatitis with multiple pseudocysts.Pancreatology. 2007;7(1):74-9. doi: 10.1159/000101881. Epub 2007 Apr 18. Pancreatology. 2007. PMID: 17449969
-
Preoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in patients with pancreatic pseudocyst associated with resolving acute and chronic pancreatitis.Ann Surg. 1989 May;209(5):532-8; discussion 538-40. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198905000-00004. Ann Surg. 1989. PMID: 2705818 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic therapy for pancreatic duct leaks and disruptions.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2013 Oct;23(4):863-92. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2013. PMID: 24079795 Review.
-
Infeasibility of endoscopic transmural drainage due to pancreatic pseudocyst wall calcifications - case report.Pol Przegl Chir. 2017 Feb 28;89(1):63-67. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0009.6006. Pol Przegl Chir. 2017. PMID: 28522785
-
Pancreatic cyst associated with pancreas divisum treated by laparoscopy-assisted cystgastrostomy in the intragastric approach: a case report and a review of the literature.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2007 Jun;17(3):317-20. doi: 10.1089/lap.2006.0091. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2007. PMID: 17570778 Review.
Cited by
-
A ruptured pancreatic pseudocyst causes acute peritonitis with clinical characteristics of a gastrointestinal tract perforation.J Surg Case Rep. 2022 May 25;2022(5):rjac164. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjac164. eCollection 2022 May. J Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35665383 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive treatment of an internal pancreaticopleural fistula with massive pleural effusion: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Sep 15;18(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04761-3. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39277749 Free PMC article.
-
Two's a Charm: Endoscopic Therapy of Multiple Pancreatic Pseudocysts.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Jan;65(1):66-70. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05947-2. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. PMID: 31732908
References
-
- Gumaste VV, Pitchumoni CS. Pancreatic pseudocyst. Gastroenterologist. 1996;4:33–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

