Gauging force by tapping tendons
- PMID: 29686281
- PMCID: PMC5913259
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03797-6
Gauging force by tapping tendons
Abstract
Muscles are the actuators that drive human movement. However, despite many decades of work, we still cannot readily assess the forces that muscles transmit during human movement. Direct measurements of muscle-tendon loads are invasive and modeling approaches require many assumptions. Here, we introduce a non-invasive approach to assess tendon loads by tracking vibrational behavior. We first show that the speed of shear wave propagation in tendon increases with the square root of axial stress. We then introduce a remarkably simple shear wave tensiometer that uses micron-scale taps and skin-mounted accelerometers to track tendon wave speeds in vivo. Tendon wave speeds are shown to modulate in phase with active joint torques during isometric exertions, walking, and running. The capacity to non-invasively assess muscle-tendon loading can provide new insights into the motor control and biomechanics underlying movement, and could lead to enhanced clinical treatment of musculoskeletal injuries and diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Four of the authors (D.G.T., J.A.M., M.S.A., and D.J.S.) are co-inventors on a pending patent application on the technology described herein. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


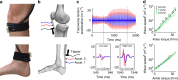

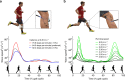
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

