Mechanisms and clinical activity of an EGFR and HER2 exon 20-selective kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29686424
- PMCID: PMC5964608
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0007-9
Mechanisms and clinical activity of an EGFR and HER2 exon 20-selective kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Mechanisms and clinical activity of an EGFR and HER2 exon 20-selective kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer.Nat Med. 2024 Sep;30(9):2694-2695. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03178-1. Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 39164519 No abstract available.
Abstract
Although most activating mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) are sensitive to available EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), a subset with alterations in exon 20 of EGFR and HER2 are intrinsically resistant and lack an effective therapy. We used in silico, in vitro, and in vivo testing to model structural alterations induced by exon 20 mutations and to identify effective inhibitors. 3D modeling indicated alterations restricted the size of the drug-binding pocket, limiting the binding of large, rigid inhibitors. We found that poziotinib, owing to its small size and flexibility, can circumvent these steric changes and is a potent inhibitor of the most common EGFR and HER2 exon 20 mutants. Poziotinib demonstrated greater activity than approved EGFR TKIs in vitro and in patient-derived xenograft models of EGFR or HER2 exon 20 mutant NSCLC and in genetically engineered mouse models of NSCLC. In a phase 2 trial, the first 11 patients with NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 mutations receiving poziotinib had a confirmed objective response rate of 64%. These data identify poziotinib as a potent, clinically active inhibitor of EGFR and HER2 exon 20 mutations and illuminate the molecular features of TKIs that may circumvent steric changes induced by these mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
J.P.R., M.B.N., and J.V.H. have filed patent applications under the Patent Cooperation Treaty and in Taiwan. J.V.H. has had grant or research support from AstraZeneca, Bayer, and GlaxoSmithKline and has served on advisory committees for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Exelixis, Genentech, GSK, Lilly, Novartis, Spectrum, and Synta. R.C.D. has licensing fees, honorarium, and travel expenses from Ariad Pharmaceuticals, has a Sponsored Research Agreement from Threshold Pharmaceuticals, and has served as an advisory Board member for AstraZeneca.
Figures

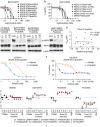
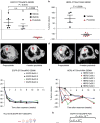
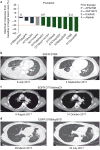
Comment in
-
Poziotinib for uncommon ERBB mutations.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018 Jul;15(7):404. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0038-7. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29743681 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bezjak A, et al. Symptom improvement in lung cancer patients treated with erlotinib: quality of life analysis of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.21. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3831–3837. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Wheatley-Price P, Ding K, Seymour L, Clark GM, Shepherd FA. Erlotinib for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in the elderly: an analysis of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.21. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2350–2357. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

