Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor: A Potential Marker for Monitoring Disease Activity in IgG4-Related Disease
- PMID: 29686532
- PMCID: PMC5854105
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6103064
Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor: A Potential Marker for Monitoring Disease Activity in IgG4-Related Disease
Abstract
Background: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory condition. T-cells play a crucial role in the pathogenesis, and therefore, serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) may be a potential biomarker.
Method: We studied the levels of sIL-2R in 26 histologically proven IgG4-RD patients with available serum sIL-2R and compared them to those in newly diagnosed and untreated sarcoidosis patients (n = 78) and controls (n = 101) and the serum sIL-2R levels in patients after treatment of IgG4-RD (n = 15). The disease activity was measured using the IgG4-Related Disease Responder Index (IgG4-RD RI).
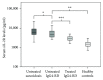
Results: Median serum sIL-2R in IgG4-RD patients was 4667 pg/ml compared to 1515 pg/ml in controls (P < 0.001) and 6050 pg/ml in sarcoidosis patients (P = 0.004 compared to IgG4-RD). All IgG4-RD patients had elevated serum sIL-2R levels compared to the reference value of <2500 pg/ml in controls and 85% elevated serum IgG4; however, these did not correlate with each other. Both serum sIL-2R and IgG4 levels declined significantly after treatment (P = 0.001 and P = 0.01, resp.). Before treatment, serum sIL-2R level and IgG4-RD RI did not correlate with each other. However, the decrease in serum sIL-2R upon treatment did correlate significantly (P = 0.04) with the decrease in disease activity assessed by IgG-RD RI.
Conclusion: Serum sIL-2R is elevated in IgG4-RD reflecting the inflammatory process with enhanced T-cell activation. Furthermore, serum sIL-2R might serve as a potential marker of response to treatment in IgG4-RD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor is a useful biomarker for disease activity but not for differential diagnosis in IgG4-related disease and primary Sjögren's syndrome adults from a defined population.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018 May-Jun;36 Suppl 112(3):157-164. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29465360
-
Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a biomarker in immunoglobulin G4-related disease.Mod Rheumatol. 2018 Sep;28(5):838-844. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2017.1416739. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Mod Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29251035
-
Value of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in sarcoidosis.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020 Jul;14(7):749-756. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2020.1751614. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32248706 Review.
-
Diagnostic Value of Serum-Soluble Interleukin 2 Receptor Levels vs Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme in Patients With Sarcoidosis-Associated Uveitis.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017 Dec 1;135(12):1352-1358. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.4771. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 29121154 Free PMC article.
-
The soluble interleukin-2 receptor: biology, function, and clinical application.Ann Intern Med. 1990 Oct 15;113(8):619-27. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-8-619. Ann Intern Med. 1990. PMID: 2205142 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Approach to IgG4-Related Retroperitoneal Fibrosis After Colorectal Cancer Surgery in a Patient With Normal IgG4 Levels: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Jul 5;16(7):e63894. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63894. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39099960 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Features and Dynamics of T Cells-Related Markers in Immunocompetent Patients with Cytomegalovirus Hepatitis.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Aug 30;2020:8874620. doi: 10.1155/2020/8874620. eCollection 2020. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32908853 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Predicts Treatment Outcome in Patients With Autoimmune Tubulointerstitial Nephritis. A Preliminary Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 25;9:827388. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.827388. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35280914 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Markers Predicting Clinical Course in Patients with IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease by Unbiased Clustering Analysis.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 17;9(12):4084. doi: 10.3390/jcm9124084. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33348892 Free PMC article.
-
The Management of IgG4-Related Disease in Children: A Systematic Review.Children (Basel). 2025 Feb 11;12(2):213. doi: 10.3390/children12020213. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003315 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karim A. F., Verdijk R. M., Guenoun J., van Hagen P., van Laar J. An inflammatory condition with different faces: immunoglobulin G4-related disease. The Netherlands Journal of Medicine. 2016;74(3):110–115. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

