Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect
- PMID: 29686713
- PMCID: PMC5857330
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6079642
Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect
Abstract
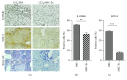
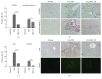
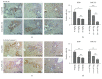
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been increasingly applied into clinical therapy. Exosomes are small (30-100 nm in diameter) membrane vesicles released by different cell types and possess the similar functions with their derived cells. Human umbilical cord MSC-derived exosomes (hucMSC-Ex) play important roles in liver repair. However, the effects and mechanisms of hucMSC-Ex on liver injury development remain elusive. Mouse models of acute and chronic liver injury and liver tumor were induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) injection, followed by administration of hucMSC-Ex via the tail vein. Alleviation of liver injury by hucMSC-Ex was determined. We further explored the production of oxidative stress and apoptosis in the development of liver injury and compared the antioxidant effects of hucMSC-Ex with frequently used hepatic protectant, bifendate (DDB) in liver injury. hucMSC-Ex alleviated CCl4-induced acute liver injury and liver fibrosis and restrained the growth of liver tumors. Decreased oxidative stress and apoptosis were found in hucMSC-Ex-treated mouse models and liver cells. Compared to bifendate (DDB) treatment, hucMSC-Ex presented more distinct antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects. hucMSC-Ex may suppress CCl4-induced liver injury development via antioxidant potentials and could be a more effective antioxidant than DDB in CCl4-induced liver tumor development.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

