Screening of Three Echinoderm Species as New Opportunity for Drug Discovery: Their Bioactivities and Antimicrobial Properties
- PMID: 29686720
- PMCID: PMC5852862
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/7891748
Screening of Three Echinoderm Species as New Opportunity for Drug Discovery: Their Bioactivities and Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
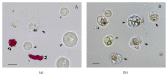
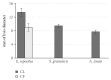
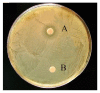
Echinoderms are a renewable resource with an economic value due to their increasing demand as food and/or source of bioactive molecules exerting antitumor, antiviral, anticoagulant, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities. In this framework, the present study is aimed at investigating the antibacterial, antioxidant, and hemolytic activities in the three Echinoderm species Echinaster sepositus, Arbacia lixula, and Sphaerechinus granularis. The sea star E. sepositus showed lysozyme-like activity (mean diameter of lysis of 13.4 ± 0.2 mm), an antimicrobial activity against the human emerging pathogens Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida famata, and a strong lytic activity (100 ± 0.05%) towards the human red blood cells. Furthermore A. lixula and E. sepositus had the highest antioxidant activity (1792.75 ± 233.7 and 1765.65 ± 484.58 nmolTE/mL, resp.). From toxicological assays, it was shown that E. sepositus was not toxic towards HeLa cells and Vibrio fischeri, encouraging the exploitation of this species in the pharmaceutical field. Therefore, our findings have implications due to the ongoing explosion of antibiotic-resistant infections because of the new opportunistic pathogens and the need to discover antibacterial agents with new modes of action. Also the recorded antioxidant activity taking into account the need to find natural antioxidants useful for human health is intriguing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
First Insight on the Mucus of the Annelid Myxicola infundibulum (Polychaeta, Sabellidae) as a Potential Prospect for Drug Discovery.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jul 5;17(7):396. doi: 10.3390/md17070396. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31284386 Free PMC article.
-
The Cœlomic Microbiota Among Three Echinoderms: The Black Sea Cucumber Holothuria forskali, the Sea Star Marthasterias glacialis, and the Sea Urchin Sphaerechinus granularis.Biology (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;14(4):430. doi: 10.3390/biology14040430. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282295 Free PMC article.
-
HPTLC fingerprint profile, in vitro antioxidant and evaluation of antimicrobial compound produced from Brevibacillus brevis-EGS9 against multidrug resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microb Pathog. 2017 Jan;102:166-172. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.12.002. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 27939872
-
Chemical Composition and Microstructural Morphology of Spines and Tests of Three Common Sea Urchins Species of the Sublittoral Zone of the Mediterranean Sea.Animals (Basel). 2020 Aug 4;10(8):1351. doi: 10.3390/ani10081351. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32759777 Free PMC article.
-
Catalysing the way towards antimicrobial effectiveness: A systematic analysis and a new online resource for antimicrobial-enzyme combinations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019 May;53(5):598-605. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019. PMID: 30639529
Cited by
-
Sea urchin (Diadema savignyi) extract as a novel protective agent against cisplatin induced neurotoxicity in rats.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023 Feb 23;24(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40360-023-00651-4. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36823675 Free PMC article.
-
First Insight on the Mucus of the Annelid Myxicola infundibulum (Polychaeta, Sabellidae) as a Potential Prospect for Drug Discovery.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jul 5;17(7):396. doi: 10.3390/md17070396. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31284386 Free PMC article.
-
Sea urchins: an update on their pharmacological properties.PeerJ. 2022 Jul 4;10:e13606. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13606. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35811815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory and Vasculoprotective Effects of Red Cell Extract from the Black Sea Urchin Arbacia lixula.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 29;15(7):1672. doi: 10.3390/nu15071672. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conand C. Fisheries and Aquaculture. II. Oxford, UK: Safran, EOLSS Publishers Co Ltd.; 2009. Commercial sea cucumbers and trepang markets; pp. 221–250.
-
- Pantazis P. A. The culture potential of Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck 1816) in Greece: A preliminary report. Aquaculture International. 2009;17(6):545–552. doi: 10.1007/s10499-008-9223-5. - DOI
-
- Furesi R., Madau F. A., Pulina P., Sai R., Pinna M. G., Pais A. Profitability and sustainability of edible sea urchin fishery in Sardinia (Italy) Journal of Coastal Conservation. 2016;20(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/s11852-016-0441-0. - DOI
-
- Ramírez-Gómez F. J., García-Arrarás J. E. Echinoderm immunity. Invertebrate Survival Journal. 2010;7(2):211–220.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

