Energy restriction, exercise and atorvastatin treatment improve endothelial dysfunction and inhibit miRNA-155 in the erectile tissue of the aged rat
- PMID: 29686722
- PMCID: PMC5902942
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-018-0265-z
Energy restriction, exercise and atorvastatin treatment improve endothelial dysfunction and inhibit miRNA-155 in the erectile tissue of the aged rat
Abstract
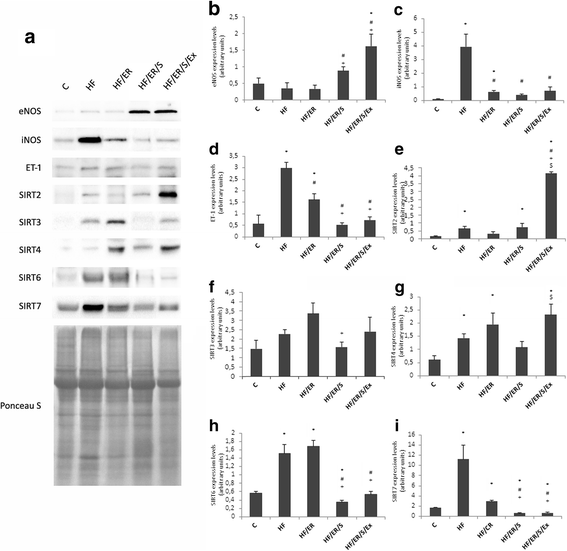
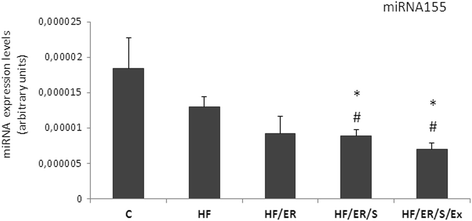
Background: Endothelial dysfunction underlies cardiovascular disease that frequently affects aged individuals. Characterized by local decrease in nitric oxide, it results from down-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression/activity. Aiming to elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved in age-related endothelial dysfunction and to unveil potential therapeutic targets, we tested how diet pattern, exercise and atorvastatin modulate the expression of eNOS, inducible NOS (iNOS), endothelin-1, sirtuins (SIRT) and microRNA-155 in the erectile tissue of high-fat fed aged rats.
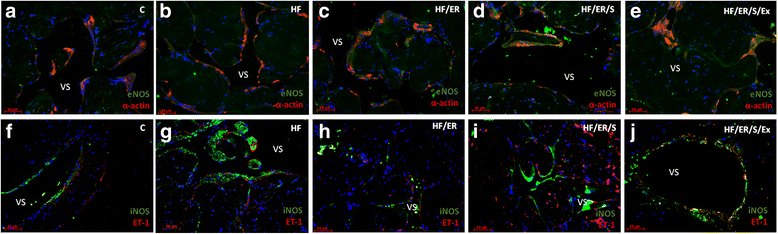
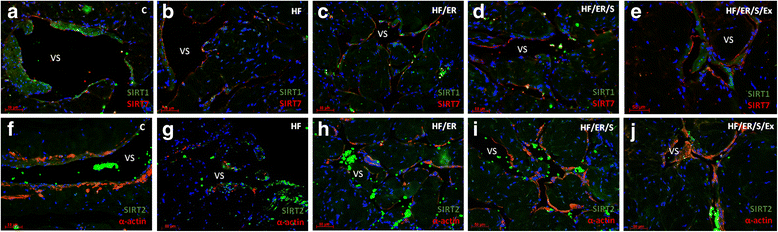
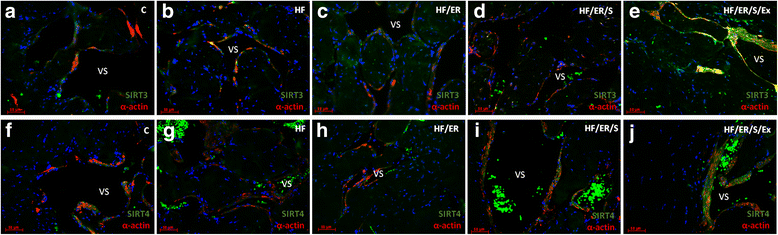
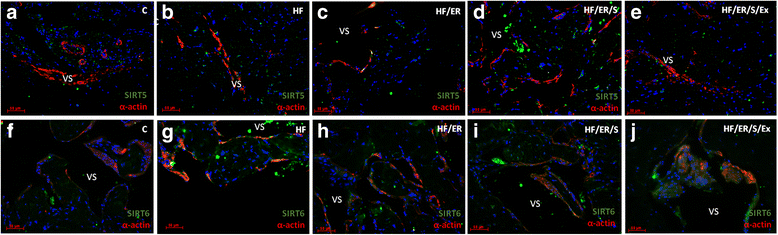
Methods: Sprague-Dawley male rats fed with high-fat diet until they completed 12 months were grouped and subjected to energy restriction (ER), ER and atorvastatin, or, ER, atorvastatin and physical exercise. Controls were fed with standard rodent chow. The blood pressure was measured using the tail-cuff method before sacrifice at 18 months. Glucose, total cholesterol, HDL, triglyceride and CRP were assessed in blood and eNOS, endothelin-1, iNOS and sirtuins were detected by immunofluorescence in the penis sections; eNOS, endothelin-1, iNOS, SIRT2-4 and SIRT6-7 were semi-quantified by western blotting in tissue homogenates. MicroRNA-155 was quantified using RT-PCR in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sections. To compare the studied variables, two-tail student t test was used.
Results: Atorvastatin promotes eNOS expression and is more efficient than ER or exercise in the control of hyperlipidemia and inflammation. Among the studied sirtuins, detected for the first time in the erectile tissue of the aged rat, SIRT2 aligns with eNOS expression. Both proteins exhibit over-expression in animals with combined exercise, atorvastatin and ER. Analysis of microRNA-155 expression also suggests its intervention in the regulation of eNOS expression. ER, particularly when combined with atorvastatin, was able to reverse the increase of iNOS and endothelin-1 in high-fat fed rats.
Conclusions: The present results indicate that the association of ER, atorvastatin and exercise is more efficient than isolated interventions in the prevention of endothelial dysfunction.
Keywords: Atorvastatin; Endothelial dysfunction; Energy restriction; Exercise; Sirtuins; microRNA-155.
Conflict of interest statement
All animals procedures were undertaken according to the European Community Guidelines (86/ 609/ EEC) and the Portuguese Act (129/ 92) for the use of experimental animals.All authors approved the final version of this manuscript.All authors declare that they have no competing interest.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Towiwat P, Phattanarudee S, Maher TJ, Ally A. Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression and cardiovascular responses during static exercise following iNOS antagonism within the ventrolateral medulla. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;398:185–194. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2218-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

