Valproic Acid Exposure of Pregnant Rats During Organogenesis Disturbs Pancreas Development in Insulin Synthesis and Secretion of the Offspring
- PMID: 29686779
- PMCID: PMC5903136
- DOI: 10.5487/TR.2018.34.2.173
Valproic Acid Exposure of Pregnant Rats During Organogenesis Disturbs Pancreas Development in Insulin Synthesis and Secretion of the Offspring
Abstract
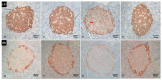
Valproic acid (VPA) plays a role in histone modifications that eventually inhibit the activity of histone deacetylase (HDAC), and will affect the expressions of genes Pdx1, Nkx6.1, and Ngn3 during pancreatic organogenesis. This experiment was designed to study the effect of VPA exposure in pregnant rats on the activity of HDAC that controls the expression of genes regulating the development of beta cells in the pancreas to synthesize and secrete insulin. This study used 30 pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats, divided into 4 groups, as follows: (1) a control group of pregnant rats without VPA administration, (2) pregnant rats administered with 250 mg VPA on day 10 of pregnancy, (3) pregnant rats administered with 250 mg VPA on day 13 of pregnancy, and (4) pregnant rats administered with 250 mg VPA on day 16 of pregnancy. Eighty-four newborn rats born to control rats and rats administered with VPA on days 10, 13, and 16 of pregnancy were used to measure serum glucose, insulin, DNA, RNA, and ratio of RNA/DNA concentrations in the pancreas and to observe the microscopical condition of the pancreas at the ages of 4 to 32 weeks postpartum with 4-week intervals. The results showed that at the age of 32 weeks, the offspring of pregnant rats administered with 250 mg VPA on days 10, 13, and 16 of pregnancy had higher serum glucose concentrations and lower serum insulin concentrations, followed by decreased concentrations of RNA, and the ratio of RNA/DNA in the pancreas. Microscopical observations showed that the pancreas of the rats born to pregnant rats administered with VPA during pregnancy had low immunoreaction to insulin. The exposure of pregnant rats to VPA during pregnancy disturbs organogenesis of the pancreas of the embryos that eventually disturb the insulin production in the beta cells indicated by the decreased insulin secretion during postnatal life.
Keywords: Gene expression; Histone deacetylase; Insulin; Pancreas organogenesis; Rat; Valproic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baynest HW. Classification, pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab. 2015;6:541. doi: 10.4172/2155-6156.1000541. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

