Laparoscopic versus Open Surgery for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of High-Quality Case-Matched Studies
- PMID: 29686975
- PMCID: PMC5852873
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1746895
Laparoscopic versus Open Surgery for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of High-Quality Case-Matched Studies
Abstract
Objective: To present a meta-analysis of high-quality case-matched studies comparing laparoscopic (LH) and open hepatectomy (OH) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: Studies published up to September 2017 comparing LH and OH for HCC were identified. Selection of high-quality, nonrandomized comparative studies (NRCTs) with case-matched design was based on a validated tool (Methodological Index for Nonrandomized Studies) since no randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were published. Morbidity, mortality, operation time, blood loss, hospital stay, margin distance, recurrence, and survival outcomes were compared. Subgroup analyses were carried out according to the surgical extension (minor or major hepatectomy).
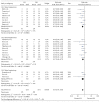
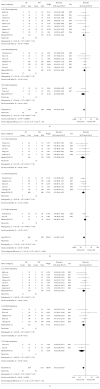
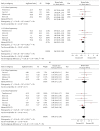
Results: Twenty studies with a total of 830 patients (388 in LH and 442 in OH) were identified. For short-term surgical outcomes, LH showed less morbidity (RR = 0.55; 95% CI, 0.47~0.65; P < 0.01), less mortality (RR = 0.43; 95% CI, 0.18~1.00; P = 0.05), less blood loss (WMD = -93.21 ml, 95% CI, -157.33~-29.09 ml; P < 0.01), shorter hospital stay (WMD = -2.86, 95% CI, -3.63~-2.08; P < 0.01), and comparable operation time (WMD = 9.15 min; 95% CI: -7.61~25.90, P = 0.28). As to oncological outcomes, 5-year overall survival rate was slightly better in LH than OH (HR = 0.66, 95% CI: 0.52~0.84, P < 0.01), whereas the 5-year disease-free survival rate was comparable between two groups (HR = 0.88, 95% CI: 0.74~1.06, P = 0.18).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis has highlighted that LH can be safely performed in selective patients and improves surgical outcomes as compared to OH. Given the limitations of study design, especially the limited cases of major hepatectomy, methodologically high-quality comparative studies are needed for further evaluation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic Versus Open Major Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2018 Oct;28(5):267-274. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000567. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2018. PMID: 30180140
-
Laparoscopic Versus Open Hepatectomy in Short- and Long-Term Outcomes of the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2019 May;29(5):643-654. doi: 10.1089/lap.2018.0588. Epub 2019 Jan 31. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2019. PMID: 30702362
-
Laparoscopic liver resection is superior to radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of propensity score-matched studies.Hepatol Int. 2024 Jun;18(3):998-1010. doi: 10.1007/s12072-024-10645-x. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Hepatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38480604
-
Laparoscopic hepatectomy versus open hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma in 157 patients: A case controlled study with propensity score matching at two Chinese centres.Int J Surg. 2018 Aug;56:203-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.06.026. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29935365
-
Meta-analysis of efficacy of laparoscopic hepatectomy versus open hepatectomy for hepatocarcinoma.J Cancer Res Ther. 2017;13(5):849-855. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_533_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29237916
Cited by
-
Outcomes and Patient Selection in Laparoscopic vs. Open Liver Resection for HCC and Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 12;15(4):1179. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041179. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults.Gut. 2024 Jul 11;73(8):1235-1268. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-331695. Gut. 2024. PMID: 38627031 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term Outcomes of Laparoscopic vs. Open Hepatectomy for Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prospective Comparative Study.Curr Med Sci. 2019 Oct;39(5):778-783. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2105-4. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Curr Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31612396
-
Laparoscopic hepatectomy for elderly patients: Major findings based on a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(30):e11703. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011703. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30045330 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Laparoscopic Hepatectomy.Front Surg. 2021 Nov 22;8:764887. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.764887. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34881286 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

