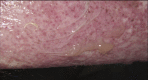
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) associated with the use of nivolumab (PD-1 inhibitor) for lymphoma
- PMID: 29687056
- PMCID: PMC5909477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.09.028
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) associated with the use of nivolumab (PD-1 inhibitor) for lymphoma
Keywords: PD-1, programmed death-1 protein; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis; adverse events; immune related; irAEs, immune-related adverse events; lymphoma; nivolumab; programmed death-1 inhibitor; toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Figures
References
-
- Weber J.S., D'Angelo S.P., Minor D. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(4):375–384. - PubMed
-
- Creamer D., Walsh S.A., Dziewulski P. UK guidelines for the management of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis in adults 2016. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174(6):1194–1227. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources