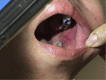
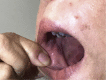
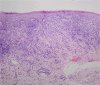
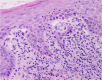
Erosive oral lichen planus after pegylated-interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 29687070
- PMCID: PMC5909481
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.09.034
Erosive oral lichen planus after pegylated-interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis B
Keywords: IFN-α; IFN-α, interferon α; LP, lichen planus; hepatitis B; interferon; oral lichen planus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exacerbation of oral erosive lichen planus by combination of interferon and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C.Int J Mol Med. 2005 Feb;15(2):237-41. Int J Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 15647837
-
Interferon gamma and interleukin 8 gene polymorphisms in patients with hepatitis C virus related oral lichen planus.Arch Oral Biol. 2018 Dec;96:189-194. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.09.015. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Arch Oral Biol. 2018. PMID: 30290294
-
Lichen planus and leukocytoclastic vasculitis induced by interferon alpha-2b in a subject with HCV-related chronic active hepatitis.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003 Mar;17(2):193-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-3083.2003.00583.x. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003. PMID: 12705750
-
[Skin diseases and hepatitis virus C infection].Med Pregl. 2000 Mar-Apr;53(3-4):141-5. Med Pregl. 2000. PMID: 10965678 Review. Croatian.
-
Oral lichen planus: a novel staging and algorithmic approach and all that is essential to know.F1000Res. 2020 Mar 24;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-206. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.18713.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32226613 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of interferon on healthy and diseased skin.Cytokine. 2020 Aug;132:154605. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.11.022. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 30527631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Friedrich R.E., Heiland M., El-Moawen A., Dogan A., von Schrenck T., Loning T. Oral lichen planus in patients with chronic liver diseases. Infection. 2003;31(6):383–386. - PubMed
-
- Maticic M., Poljak M., Lunder T., Rener-Sitar K., Stojanovic L. Lichen planus and other cutaneous manifestations in chronic hepatitis C: pre- and post-interferon-based treatment prevalence vary in a cohort of patients from low hepatitis C virus endemic area. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22(7):779–788. - PubMed
-
- Remmerbach T.W., Liese J., Krause S. No association of oral lichen planus and hepatitis C virus infection in central Germany. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(1):193–197. - PubMed
-
- Dalekos G.N., Christodoulou D., Kistis K.G., Zervou E.K., Hatzis J., Tsianos E.V. A prospective evaluation of dermatological side-effects during alpha-interferon therapy for chronic viral hepatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998;10(11):933–939. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
