High-Fat Diets Alter the Modulatory Effects of Xenobiotics on Cytochrome P450 Activities
- PMID: 29688711
- PMCID: PMC7075635
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.8b00008
High-Fat Diets Alter the Modulatory Effects of Xenobiotics on Cytochrome P450 Activities
Abstract
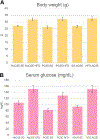
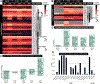
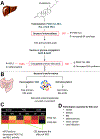
Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (P450) enzymes metabolize critical endogenous chemicals and oxidize nearly all xenobiotics. Dysregulated P450 activities lead to altered capacity for drug metabolism and cellular stress. The effects of mixed exposures on P450 expression and activity are variable and elusive. A high-fat diet (HFD) is a common exposure that results in obesity and associated pathologies including hepatotoxicity. Herein, we report the effects of cigarette smoke on P450 activities of normal weight and HFD induced obese mice. Activity-based protein profiling results indicate that HFD mice had significantly decreased P450 activity, likely instigated by proinflammatory chemicals, and that P450 enzymes involved in detoxification, xenobiotic metabolism, and bile acid synthesis were effected by HFD and smoke interaction. Smoking increased activity of all lung P450 and coexposure to diet effected P450 2s1. We need to expand our understanding of common exposures coupled to altered P450 metabolism to enhance the safety and efficacy of therapeutic drug dosing.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. (2014) Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014, Geneva.
-
- Tarantino G, Conca P, Basile V, Gentile A, Capone D, Polichetti G, and Leo E (2007) A prospective study of acute drug-induced liver injury in patients suffering from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Res 37, 410–415. - PubMed
-
- Michaut A, Moreau C, Robin MA, and Fromenty B (2014) Acetaminophen-induced liver injury in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int 34, e171–179. - PubMed
-
- Cheymol G (2000) Effects of obesity on pharmacokinetics implications for drug therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet 39, 215–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

