Zebrafish-based identification of the antiseizure nucleoside inosine from the marine diatom Skeletonema marinoi
- PMID: 29689077
- PMCID: PMC5916873
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196195
Zebrafish-based identification of the antiseizure nucleoside inosine from the marine diatom Skeletonema marinoi
Abstract
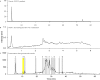
With the goal of identifying neuroactive secondary metabolites from microalgae, a microscale in vivo zebrafish bioassay for antiseizure activity was used to evaluate bioactivities of the diatom Skeletonema marinoi, which was recently revealed as being a promising source of drug-like small molecules. A freeze-dried culture of S. marinoi was extracted by solvents with increasing polarities (hexane, dichloromethane, methanol and water) and these extracts were screened for anticonvulsant activity using a larval zebrafish epilepsy model with seizures induced by the GABAA antagonist pentylenetetrazole. The methanolic extract of S. marinoi exhibited significant anticonvulsant activity and was chosen for bioassay-guided fractionation, which associated the bioactivity with minor constituents. The key anticonvulsant constituent was identified as the nucleoside inosine, a well-known adenosine receptor agonist with previously reported antiseizure activities in mice and rat epilepsy models, but not reported to date as a bioactive constituent of microalgae. In addition, a UHPLC-HRMS metabolite profiling was used for dereplication of the other constituents of S. marinoi. Structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated by nuclear magnetic resonance and high-resolution spectrometry. These results highlight the potential of zebrafish-based screening and bioassay-guided fractionation to identify neuroactive marine natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Megiddo I, Colson A, Chisholm D, Dua T, Nandi A, Laxminarayan R. Health and economic benefits of public financing of epilepsy treatment in India: An agent-based simulation model. Epilepsia. 2016;57(3):464–74. doi: 10.1111/epi.13294 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wahab A. Difficulties in treatment and management of epilepsy and challenges in new drug development. Pharmaceuticals. 2010;3(7):2090–110. doi: 10.3390/ph3072090 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santulli L, Coppola A, Balestrini S, Striano S. The challenges of treating epilepsy with 25 antiepileptic drugs. Pharmacol Res. 2016;107:211–9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schachter SC. Botanicals and Herbs: A traditional approach to treating epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics. 2009;6(2):415–20. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2008.12.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Afrikanova T, Serruys AS, Buenafe OE, Clinckers R, Smolders I, de Witte PA, et al. Validation of the zebrafish pentylenetetrazol seizure model: locomotor versus electrographic responses to antiepileptic drugs. Plos One. 2013;8(1):e54166 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054166 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

