Research Progress on Rolling Circle Amplification (RCA)-Based Biomedical Sensing
- PMID: 29690513
- PMCID: PMC6027247
- DOI: 10.3390/ph11020035
Research Progress on Rolling Circle Amplification (RCA)-Based Biomedical Sensing
Abstract
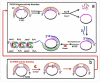
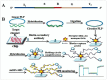
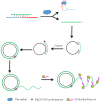
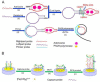
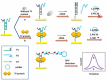
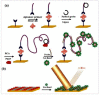
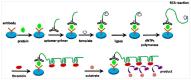
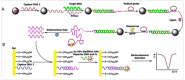
Enhancing the limit of detection (LOD) is significant for crucial diseases. Cancer development could take more than 10 years, from one mutant cell to a visible tumor. Early diagnosis facilitates more effective treatment and leads to higher survival rate for cancer patients. Rolling circle amplification (RCA) is a simple and efficient isothermal enzymatic process that utilizes nuclease to generate long single stranded DNA (ssDNA) or RNA. The functional nucleic acid unit (aptamer, DNAzyme) could be replicated hundreds of times in a short period, and a lower LOD could be achieved if those units are combined with an enzymatic reaction, Surface Plasmon Resonance, electrochemical, or fluorescence detection, and other different kinds of biosensor. Multifarious RCA-based platforms have been developed to detect a variety of targets including DNA, RNA, SNP, proteins, pathogens, cytokines, micromolecules, and diseased cells. In this review, improvements in using the RCA technique for medical biosensors and biomedical applications were summarized and future trends in related research fields described.
Keywords: biosensor; cancer; clinical diagnostics; rolling circle amplification (RCA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Li Y., Zeng Y., Ji X., Li X., Ren R. Cascade signal amplification for sensitive detection of cancer cell based on self-assembly of DNA scaffold and rolling circle amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012;171–172:361–366. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2012.04.060. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

