Identification of a neuronal population in the telencephalon essential for fear conditioning in zebrafish
- PMID: 29690872
- PMCID: PMC5978991
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-018-0502-y
Identification of a neuronal population in the telencephalon essential for fear conditioning in zebrafish
Abstract
Background: Fear conditioning is a form of learning essential for animal survival and used as a behavioral paradigm to study the mechanisms of learning and memory. In mammals, the amygdala plays a crucial role in fear conditioning. In teleost, the medial zone of the dorsal telencephalon (Dm) has been postulated to be a homolog of the mammalian amygdala by anatomical and ablation studies, showing a role in conditioned avoidance response. However, the neuronal populations required for a conditioned avoidance response via the Dm have not been functionally or genetically defined.
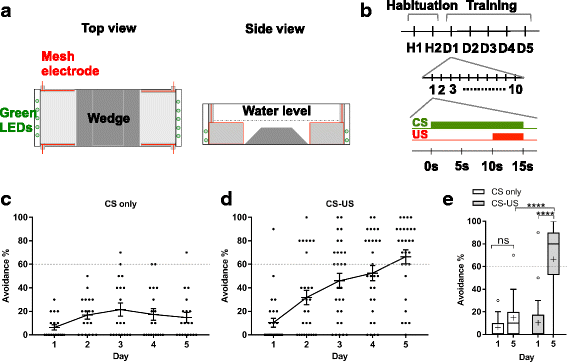
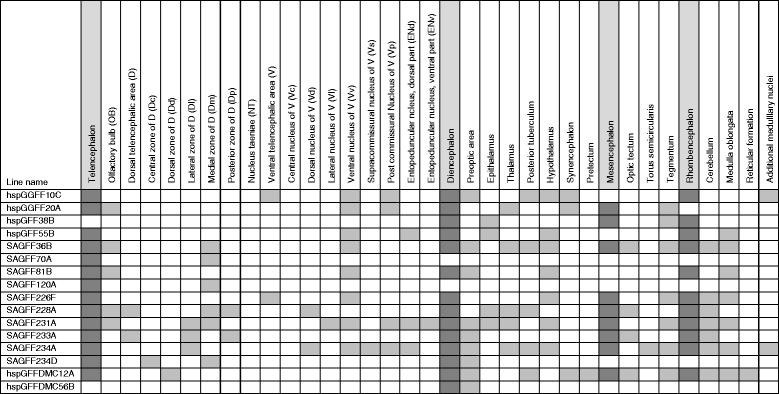
Results: We aimed to identify the neuronal population essential for fear conditioning through a genetic approach in zebrafish. First, we performed large-scale gene trap and enhancer trap screens, and created transgenic fish lines that expressed Gal4FF, an engineered version of the Gal4 transcription activator, in specific regions in the brain. We then crossed these Gal4FF-expressing fish with the effector line carrying the botulinum neurotoxin gene downstream of the Gal4 binding sequence UAS, and analyzed the double transgenic fish for active avoidance fear conditioning. We identified 16 transgenic lines with Gal4FF expression in various brain areas showing reduced performance in avoidance responses. Two of them had Gal4 expression in populations of neurons located in subregions of the Dm, which we named 120A-Dm neurons. Inhibition of the 120A-Dm neurons also caused reduced performance in Pavlovian fear conditioning. The 120A-Dm neurons were mostly glutamatergic and had projections to other brain regions, including the hypothalamus and ventral telencephalon.
Conclusions: Herein, we identified a subpopulation of neurons in the zebrafish Dm essential for fear conditioning. We propose that these are functional equivalents of neurons in the mammalian pallial amygdala, mediating the conditioned stimulus-unconditioned stimulus association. Thus, the study establishes a basis for understanding the evolutionary conservation and diversification of functional neural circuits mediating fear conditioning in vertebrates.
Keywords: Gal4-UAS; Pavlovian conditioning; amygdala; botulinum neurotoxin; dorsomedial telencephalon; enhancer trapping; fear conditioning; gene trapping; transposable element.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
This experiment was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC, approval identification number 27–2), and complied with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the IACUC.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures








References
-
- Martinez-Garcia F, Novejarque A, Lanuza E. The evolution of the amygdala in vertebrates. In: Kaas JH, editor. Evolutionary Neuroscience. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press; 2009. pp. 313–392.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

