Understanding influences on the uptake of pulmonary rehabilitation in the East of England: an Inclusive Design/mixed-methods study protocol
- PMID: 29691248
- PMCID: PMC5922519
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020750
Understanding influences on the uptake of pulmonary rehabilitation in the East of England: an Inclusive Design/mixed-methods study protocol
Abstract
Introduction: 1.2 million people in the UK have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that causes breathlessness, difficulty with daily activities, infections and hospitalisation. Pulmonary rehabilitation (PR), a programme of supervised exercise and education, is recommended for patients with COPD. However, only 1 in 10 of those who need it receive PR. Also, the UK National COPD Audit Programme concluded that the COPD treatment might not be accessible to people with disabilities. This paper applies an Inclusive Design approach to community-based PR service provisions. It aims to inform improvements to the PR service by identifying barriers to the uptake of PR in the COPD care journey in relation to patients' capabilities that can affect their access to PR.
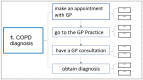
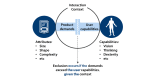
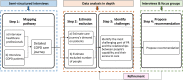
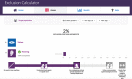
Methods and analysis: The protocol includes four steps. Step 1 will involve interviews with healthcare professionals and patients to gather insight into their experiences and produce a hierarchical task analysis of the COPD care journeys. Step 2 will estimate the service exclusion: the demand of every task on patients' capabilities will be rated by predefined scales, and the proportion of the population excluded from the service will be estimated by an exclusion calculator. Step 3 will identify the challenges of the PR service; a framework analysis will guide the data analysis of the interviews and care journey. Step 4 will propose recommendations to help patients manage their COPD care informed by the challenges identified in step 3 and refine recommendations through interviews and focus groups.
Ethics and dissemination: The Cambridge Central Research Ethics Committee gave the study protocol a positive ethical opinion (17/EE/0136). Study results will be disseminated through peer-reviewed journals, conferences and the British Lung Foundation networks. They will also be fed into a Research for Patient Benefit project on increasing the referral and uptake of PR.
Keywords: COPD; care journey; inclusive design; patient-centred design; patients’ capability; pulmonary rehabilitation.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs315/en/ (accessed 20 May 2016).
-
- British Lung Foundation. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) statistics. http://statistics.blf.org.uk/copd (accessed 20 May 2016).
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. COPD Costing Report. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, 2011.
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. COPD Guideline CG101. 2010. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/CG101 (accessed 20 May 2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
